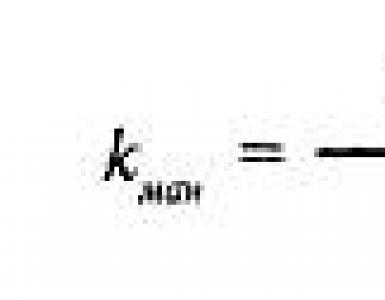Financial resources of the enterprise and financial obligations. Financial resources of the enterprise: own and borrowed
Currently, the Russian economy faces major challenges. In this regard, several questions become relevant at once. All of them, to one degree or another, relate to financial resources.
Relevance of the problem
Material and financial resources today are of paramount importance for economic development. The intensity of market relations requires a stable injection of funds into all areas of economic activity. The financial resources of the state are of particular importance. Their condition, in turn, depends on the profitability of companies operating in the country. The existing problems are due to various reasons. They are associated with changes that occur in the credit and banking structure and the periodic deepening of inflation and crisis processes. All this negatively affects the financial resources of the state in general, and the state of capital of companies in particular.
Raising funds
Managing financial resources requires a competent approach. Today this is one of the most important tasks for all business entities. In addition to the fact that one’s own financial resources are involved, there is a need to attract third-party borrowed funds. However, this process can only produce results if a rational relationship between these flows is observed. In this regard, it is necessary to create a scientifically based capital allocation policy that would take into account the specifics of the activities of entities within the modern market.
Financial resources of the enterprise
The capital of an economic entity represents the foundation of its creation and subsequent development. In the process of operation, these funds ensure the interests of the owner and his staff. At the same time, capital also participates in state financial circulation. Each business entity must have certain funds aimed at meeting its needs. The financial resources of an enterprise are a complex that includes two elements. First of all, these are the funds that the company itself has. In addition, firms also attract borrowed financial resources. This complex is aimed at fulfilling obligations, current costs, and expenses related to capital expansion. It acts as a result of the interaction of receipt, distribution and expenditure of funds, accumulation and subsequent implementation in the course of economic activity.  To create capital, different sources of financial resources are used. Funds come from investors, founders, owners, investment funds, commercial banks and so on. The subsequent formation of financial resources is carried out in companies through depreciation charges and profits. This, however, does not exclude the attraction of additional issues, bonds, shares and other securities for circulation, obtaining loans and other loans.
To create capital, different sources of financial resources are used. Funds come from investors, founders, owners, investment funds, commercial banks and so on. The subsequent formation of financial resources is carried out in companies through depreciation charges and profits. This, however, does not exclude the attraction of additional issues, bonds, shares and other securities for circulation, obtaining loans and other loans.
Purpose of funds
The financial resources of an organization are of paramount importance in the process of reproduction and its regulation, stimulation of economic activity and enhancing its effectiveness. In general, working capital helps to ensure control over the general condition of an economic entity. One of the main tasks of managers is the competent use of financial resources. Specialists must determine the most promising areas for their distribution and ensure income generation on their basis. Thus, the financial resources of the organization perform control, stimulating, distribution, regulatory and reproduction functions.
Basic requirements for funds
To ensure the efficiency of financial resources, any company needs to:
- Mobilize funds. This ensures their maneuverability and allows them to concentrate on the most important areas of economic activity.
- Develop plans in accordance with which the formation of sources of financial resources, the actual receipt of funds, distribution for the coming and long-term periods will be carried out.
- Maintain certain proportions between spending funds and receiving them.
Classification
The sources of financial resources of an enterprise include all receipts and cash income available to a company or other business entity for a certain period. They are aimed at making contributions and expenses that are necessary for social and industrial development. In addition to those listed above, the following sources of financial resources of the enterprise are involved in the turnover:
- Budgets of different levels.
- Special centralized funds.
Available and incoming funds are used to advance current costs, investments, deductions and expenses for social and other needs, and so on. Sources of financial resources are divided into several categories:
- Off-budget centralized funds.
- Attracted on a non-refundable or refundable basis.
- Budget revenues.
- Borrowed funds.
- Equity.

The accumulation of funds is carried out primarily through profits from the main and other (additional) activities, income from the sale of retired material assets, an increase in sustainable liabilities, depreciation, loans and credits, shares and other contributions from employees, and various targeted income. Sources of financial resources include concerns and associations, which, in turn, include the company and higher structures, while maintaining industry-specific state regulatory bodies. In the latter case, funds come in the form of insurance payments and subsidies. The formation of the enterprise's financial resources is thus carried out through redistribution. In this group, insurance payments are becoming increasingly important, and budget revenues, directed strictly to targeted needs, are becoming increasingly important.
Inclusion of funds into circulation
Financial resources can be used for various purposes. The main ones include:
- Ensuring current production and sales processes for stable production and trading activities. This is achieved through planned allocations of funds to core and support operations, marketing, supplies and distribution.
- Financing of management activities that help maintain the functionality of the administrative and organizational system at a high level. This task is achieved through restructuring, introducing new services or reducing the existing staff.
- Investing in core production. In this direction, various methods of financial resources are used. In particular, the most promising are short- and long-term investments in the complete renewal and modernization of production processes, the creation of new directions or the reduction of unprofitable ones.
- Investments in production that bring the company more income than its own activities. We are talking, in particular, about the acquisition of securities and other assets in different sectors of the market, investing in the capital of other companies to obtain profit and rights to participate in their management systems or in projects with a high degree of risk and profitability, and providing loans to other corporations.
- Creation of reserves. Such sources of financial resources are formed both by the company itself and by insurance companies and budget funds, based on regulatory contributions, which, in turn, contribute to maintaining a continuous circulation of funds and protecting the corporation from unfavorable changes in market conditions.
Company capital
Financial resources that belong directly to the corporation itself are, as a rule, determined by the minimum need for funds to create the necessary inventory base, ensure planned production and sales volumes, as well as to perform calculations and make transfers on time. The company's capital is formed from the value of the property invested by the owner. It represents the difference between liabilities (liabilities) and total assets - the amount of excess of the market price of tangible assets over outstanding debt. 
Benefits of Capital
Financial resources owned by the company, as opposed to borrowed funds, have the following advantages:
- Ease of attraction. Decisions related to increasing capital, especially from internal sources, are made by managers and owners of the enterprise without coordination with other business entities.
- High ability to generate profits in all areas of activity. This is due to the fact that the use of these financial resources does not require the payment of loan interest.
- Ensuring monetary stability in the process of company development, corporate solvency in long-term periods. This, in turn, helps reduce the risk of bankruptcy.
Disadvantages of Capital
In addition to the advantages, financial resources owned directly by the corporation have the following disadvantages:
- Limited volume of attraction. This, in turn, significantly reduces the opportunities for expanding the company's investment and operating activities during favorable periods of market conditions and at certain stages of its life cycle.
- High cost compared to alternative borrowed funds.
- An unused opportunity to increase the return on capital ratio due to the receipt of loans and credits, since without them it is impossible to ensure that financial profitability exceeds economic profitability.
Capital structure
Financial resources owned by the corporation provide stability, but at the same time they cannot ensure the creation of the necessary additional volumes during favorable market conditions. The company's funds include retained earnings, reserve, additional, authorized capital and other assets. All these elements are undoubtedly important in the activities of a corporation, but are not sufficient to obtain maximum returns.
Authorized capital
It represents the start-up funds that are necessary for the company to carry out its main activities in order to generate income. Statutory contributions can be made in money and property, which the company participants transfer to pay off obligations. The main difference between these assets is that they must be distributed among the founders. In this regard, the decision on changes adopted at the general meeting must be accompanied by the establishment of the procedure for applying them to each participant. The authorized capital represents the property core activity of the company. It ensures that the share of each founder in the management of the corporation is established, and also guarantees that the interests of creditors are respected. 
Additional products
This capital consists of share premium, which is created in the JSC. Additional funds represent the amount of excess of the selling price of shares in relation to the nominal value in the process of open subscription. Share premium, which arises during the creation of authorized capital in joint-stock companies, cannot be used for the consumer needs of the company. Additional capital is also formed from:
- Amounts of additional valuation of non-current assets.
- Exchange rate differences associated with the formation of authorized capital.
- Amounts of retained income used as sources to cover capital investments.
- Property received free of charge, except that which relates to the social sphere and is included in retained earnings.
- Funds from budgetary allocations to finance long-term deposits.
 Replenishment of additional capital can be carried out using funds that are used to replenish the company's working capital. This source is formed during the distribution of retained earnings by the founders. Budget funds are credited to a special account, from which they are subsequently written off to pay off expenses incurred in accordance with the corporation's investment program. After this, the amount spent is included in additional capital. The basis for such accession is the use of budget allocations for their intended purpose. Typically, part of the capital that arises upon the receipt of a certain type of property or an increase in its price is used to cover expenses in connection with the disposal of similar material assets or a decrease in their value.
Replenishment of additional capital can be carried out using funds that are used to replenish the company's working capital. This source is formed during the distribution of retained earnings by the founders. Budget funds are credited to a special account, from which they are subsequently written off to pay off expenses incurred in accordance with the corporation's investment program. After this, the amount spent is included in additional capital. The basis for such accession is the use of budget allocations for their intended purpose. Typically, part of the capital that arises upon the receipt of a certain type of property or an increase in its price is used to cover expenses in connection with the disposal of similar material assets or a decrease in their value.
Reserve
This element represents the company's insurance capital, which is intended to reimburse general balance sheet costs in the absence of other options for covering them. Reserve funds are also used to pay income to creditors and investors if there is not enough profit to pay off these obligations. These resources guarantee the smooth operation of the enterprise and respect for the interests of third parties. The latter, in turn, gain confidence in the solvency of the company. Accounting for the creation of reserve funds provides the information necessary to monitor compliance with its lower and upper limits. Regardless of the situation, the maximum amount of this capital should not exceed the amount determined by the owners and which is recorded in the constituent documentation. The law, at the same time, establishes its minimum limit for joint ventures and joint stock companies.
Special funds
This form of company equity is considered quite unique and very promising. Special funds are created for subsequent targeted use. Companies can create such reserves for:
- Payment for upcoming employee vacations.
- Calculation of an annual bonus for long service.
- Upcoming expenses for repairs of property intended for rental in accordance with the rental agreement.
- Payment of remuneration at the end of the year.
- Carrying out OS repairs.
- Production costs for training during the seasonal nature of the activity.
- Upcoming costs for environmental protection measures (land reclamation, etc.).
- Warranty service and repair.
- Covering other foreseen expenses and other purposes provided for in the legislation of the Russian Federation and regulations of the Ministry of Finance.
Consumer and savings funds
They belong to special reserves. The accumulation fund is considered to be funds that are used for the production development of the company or other similar needs that are provided for in the constituent documentation. For example, this could be the creation of new property. Consumer funds consist of funds reserved for social development activities (except for capital investments), material incentives for personnel and other works of a similar nature that do not lead to the formation of new material assets.
retained earnings
It characterizes part of the company’s income received in the previous period and not used for consumption by shareholders/shareholders/owners and employees. Retained earnings are calculated as the difference between all financial results identified from operations (based on accounting) and the assessment of balance sheet items for the reporting period and the mandatory amount of fees and taxes, including sanctions for violations. This part of the income is intended for reinvestment (capitalization) of production development. In terms of economic content, retained earnings act as one of the types of reserves of the corporation's own funds. 
Third party financial resources
These primarily include borrowed funds. They characterize the total amount of monetary obligations of the company. Borrowed funds can be long-term or short-term. The latter includes all resources attracted for a period of up to a year. The main forms of these loans include short-term bank loans, various accounts payable (for services, products, work, bills issued, wages, and so on). As a rule, obligations arise to suppliers or note holders. Long-term funds are raised for a period of more than a year. Their main forms include long-term loans, debt on issued bonds, financial assistance that was provided on a repayable basis, and so on.
Involved funds
This is another type of additional income used in turnover, in addition to equity and borrowed capital. Raised funds consist of accounts payable and earmarked money before they are put into circulation for their intended purpose. A set of financial obligations arises during the current activities of the company. In the work of a corporation, debt may arise to contractors, which include contractors and suppliers, the budget, employees, dependent and subsidiary structures, extra-budgetary social services. funds and so on. Managing these funds requires an individual approach to creditors. In accordance with this, a settlement scheme with them is built.
In modern conditions, the role of finance in the functioning of enterprises in the economic system is growing. Enterprises use certain types of resources to carry out business activities, generate income and savings: material, labor, financial, as well as. Among the named economic categories, the most complex is the category of “financial resources”. There is still no generally accepted point of view among academic economists about the essence of this category. However, many economists believe that “financial resources” are the funds available to enterprises.
However, money is an independent economic category. The funds of enterprises located in accounts at bank institutions, cash desks, etc. are invested in their concept. They are taken into account in the accounting records of enterprises and are reflected in the assets of their balance sheet.
Financial resources are sources of funds for enterprises, directed towards the formation of their assets. These sources can be our own, borrowed or attracted. They are reflected in the relevant sections.
The concept of financial resources was introduced for the first time when drawing up the first five-year plan of the USSR, which included a balance of financial resources.
According to P.I. Vakhrin, the financial resources of an enterprise are cash income and receipts at the disposal of a business entity and intended to fulfill the financial obligations of the enterprise, finance current costs and costs associated with the expansion of production, as well as for economic stimulation of the enterprise’s employees.
P.A. Levchaev understands financial resources as current and potential funds, which, if necessary, can be used as signs of distributed value, i.e. cash, non-cash form of money, securities, etc.
Financial assets are funds that can be immediately used by an enterprise as signs of value that characterize its movement. Financial resources are a more capacious concept, including, along with financial resources (to ensure current activities) and potential ones that can be obtained if necessary. This provision is based on the fact that the activities of the enterprise are not limited to the current time and can be planned for the future.
Financial resources are the economic basis for organizing trading activities on the principles of self-financing. This means that the most important task of enterprises is to find reserves to increase their own financial resources and improve their use in order to increase the efficiency of the enterprise as a whole.
The formation of financial resources is carried out at two levels: nationwide and at each enterprise. The source of formation of financial resources at the national level is.
The sources of formation of the enterprise’s financial resources are:
A) own funds and equivalent funds (profit from the sale of disposed property, stable liabilities);
b) resources mobilized for;
c) receipts of funds from financial redistribution (insurance compensation; receipts from concerns, associations, industry structures; share contributions; and interest on securities; budget subsidies).
The formation of financial resources is carried out in the process of creating enterprises and implementing them in the implementation of economic and financial activities.
When creating enterprises, the sources of financial resources depend on the form of ownership on the basis of which the enterprise is created. Thus, when creating state-owned enterprises, financial resources are formed from the budget, funds from higher management bodies, funds from other similar enterprises during their reorganization, etc. When creating collective enterprises, they are formed from share (equity) contributions of the founders, voluntary contributions from legal entities and individuals and etc. All these contributions (funds) represent the authorized (initial) capital and are accumulated in the authorized capital of the created enterprise.
Additional capital is the amount of additional valuation as a result of an increase in the value of non-current assets due to their revaluation; income, i.e. the amount of excess of the sale price of shares over shares from their additional issue. Additional capital can be used to increase the authorized capital, repay the balance sheet loss for the reporting year, as well as for other purposes.
Retained earnings - not distributed in the form of dividends between the founders and not used for consumption by the owners and staff. The amount of retained earnings indicates the organization's ability to finance itself.
Targeted financing is the amount of targeted revenues received from the budget.
Thus, the authorized capital and additional sources of financing formed during the operation of the enterprise form it, i.e. it is the difference between an organization's total assets and its liabilities. Own financial resources include profit remaining at the disposal of the organization and depreciation charges.
Significant financial resources can be mobilized in the financial market. The forms of their mobilization can be: the sale of shares and other types of securities, as well as credit investments.
Funds received from the financial and banking system in the order of redistribution include insurance compensation; receipts from concerns, associations, industry structures; share contributions; dividends and interest on securities; budget subsidies.
In addition to equity capital, the financial resources of enterprises are formed from attracted and borrowed sources.
The attracted financial resources include for goods, works, services, as well as all types of current obligations of the enterprise for settlements:
The amount of advances received from legal entities and individuals for subsequent deliveries of products, performance of work, provision of services;
- the amount of debt of the enterprise for all types of payments to the budget, including taxes withheld from employee income;
- arrears of contributions to extra-budgetary funds;
- the enterprise’s debt to pay dividends to its founders;
- the amount that the enterprise issued to suppliers and contractors to ensure the supply of products, performance of work, provision of services, etc.
Borrowed financial resources include long-term and short-term bank loans, as well as other long-term financial obligations associated with raising borrowed funds (except for bank loans), on which interest is charged, etc.
Another form of borrowing is. Leasing is an operation for the placement of movable and immovable property, which is specially purchased by a leasing company, remains its property, but is leased to entrepreneurs.
Own, borrowed and attracted capital, which forms, on the one hand, the financial resources of the enterprise and takes part in the financing of their assets, on the other hand, it represents obligations (long-term and short-term) to specific owners - the state, legal entities and individuals.
The composition and structure of sources of financial resources is not a constant once and for all. They depend on the state of the enterprise’s economy, the characteristics of the formation of reserves and costs and can change over time.
So, the composition of financial resources and their volumes depend on the type and size of the enterprise, the type of its activity, and the volume of production. At the same time, the volume of financial resources is closely related to the volume of production and the effective operation of the enterprise. The greater the production volume and the higher the efficiency of the enterprise, the greater the amount of its own financial resources, and vice versa.
The financial resources of an enterprise are the totality of its own cash income and receipts from outside, intended to fulfill the financial obligations of the enterprise, finance current costs and costs associated with the development of production.
It is worth highlighting such a concept as capital - part of the financial resources invested in production and generating income upon completion of the turnover. In other words, capital acts as a converted form of financial resources.
Financial resources by source of education are divided into own (internal) and attracted on different terms (external), mobilized in the financial market and received in the order of redistribution.
Own financial resources include: income, profit from core activities, profit from other activities, proceeds from the sale of disposed property, less expenses for its sale, depreciation charges.
It should be remembered that not all profits remain at the disposal of the enterprise; part of it in the form of taxes and other tax payments goes to the budget. The profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise is distributed by decision of the governing bodies for the purposes of accumulation and consumption. Profit allocated for accumulation is used for the development of production and contributes to the growth of the enterprise's property. Profits allocated for consumption are used to solve social problems.
Depreciation charges are the monetary expression of the cost of depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets. They have a dual nature, since they are included in the cost of production and, as part of the proceeds from the sale of products, go to the current account of the enterprise, becoming an internal source of financing for both simple and expanded reproduction.
Attracted, or external, sources of financial resources can be divided into own, borrowed, redistributed and budgetary allocations. This division is determined by the form of capital investment. If external investors invest money as an entrepreneur
body's capital, then the result of such an investment is the formation of attracted own financial resources.
Entrepreneurial capital is capital invested in the authorized capital of another enterprise for the purpose of making a profit or participating in the management of the enterprise.
Loan capital is transferred to the enterprise for temporary use on the terms of payment and repayment in the form of bank loans issued for different periods, funds from other enterprises in the form of bills, bond issues.
Funds raised in the financial market include: funds from the sale of own shares and bonds, as well as other types of securities.
The funds received through redistribution will consist of: insurance compensation for risks incurred, financial resources coming from concerns, associations, parent companies, dividends and interest on securities of other issuers, budget subsidies.
Budget allocations can be used both on a non-refundable and repayable basis. As a rule, they are allocated to finance government orders, individual investment programs, or as short-term government support for enterprises whose production is of national importance.
Financial resources are used by the enterprise in the process of production and investment activities. They are in constant motion and are in cash form only in the form of cash balances in a current account in a commercial bank and in the cash register of an enterprise.
An enterprise, taking care of its financial stability and stable place in the market economy, distributes its financial resources by type of activity and over time. The deepening of these processes leads to the complication of financial work and the use of special financial instruments in practice.
More on the topic Financial resources of an enterprise:
- The concept of financial resources of an enterprise and the principles of their formation
- Methodological features of effective management of enterprise financial resources
- The use of financial resources and their role in ensuring the reproduction process in the enterprise
- The role of the financial market in the mobilization and distribution of financial resources of enterprises
- Main tasks and features of managing financial resources of a small enterprise
- A credit and financial analysis of your enterprise should be carried out in comparison with the economic and financial activities of other enterprises in the industry and competitors. This is the only way to get an objective idea of the company’s capabilities in the present and future.
Own means of generating financial resources primarily include the authorized capital of an enterprise. Own resources are considered the most reliable, since self-financing reduces the risk of bankruptcy and has certain advantages over competitors.
The authorized capital of an enterprise determines the minimum amount of its property, which guarantees the interests of its creditors. It represents the amount of contributions made by the founders of an economic entity to ensure its livelihoods. The authorized capital is the initial formation of financial resources. Its minimum amount is determined by the legally established minimum amount of payment in the country. The size of the authorized capital is fixed in the charter or constituent document of the enterprise, which is subject to registration in the prescribed manner. The following can be contributed to the authorized capital: buildings, equipment, securities, rights to use natural resources and other property rights, and funds. The cost of deposits is assessed in rubles by a joint decision of participants of economic entities and constitutes their shares in the authorized capital.
The next source of the enterprise’s own funds is additional capital, which includes the following:
Results of revaluation of fixed assets;
Share premium (income from the sale of shares in excess of their par value minus their expenses for their sale);
Funds and material assets received free of charge for production purposes;
Allocation from the budget to finance capital investments;
Income for replenishment of working capital.
Additional capital accumulates funds received by the enterprise during the year from the above-mentioned capitals. The main source here is the results of the revaluation of fixed assets. It is quite natural to increase your own funds annually due to additional capital.
The main source of financial resources in operating enterprises is the cost of products sold (services provided), various parts of which, in the process of revenue distribution, take the form of cash income and savings.
Financial resources are mainly formed mainly from profits (from core and other activities) and depreciation charges.
The enterprise's reserve capital is formed from profits. The reserve capital is intended to cover its losses. According to world practice, it should also be used in two directions:
If there is a lack of working capital, it is directed to the formation of inventories, work in progress and finished products;
If there is sufficient working capital, it is directed to short-term financial investments.
There are additional sources of self-financing for the enterprise:
Reserves for upcoming expenses and payments;
Revenue of the future periods.
These sources of funds relate to second-priority obligations created by the enterprise independently.
Own sources of financing are characterized by the following main positive aspects:
Ease of attraction, since decisions related to increasing equity capital are made by the owners and managers of the enterprise without economic entities;
Higher ability to generate profit in all areas of activity, since its use does not require payment of loan interest in all its forms;
Ensuring the financial sustainability of the enterprise’s development, its solvency in the long term, and, accordingly, reducing the risk of bankruptcy.
However, it has the following disadvantages:
Limitation of the volume of attraction, and, consequently, the possibility of significantly expanding the operating and investment activities of the enterprise during periods of favorable market conditions and at certain stages of its life cycle;
High cost in comparison with alternative borrowed sources of capital formation;
Unused opportunity to increase the return on equity ratio by attracting borrowed funds.
When internal sources of financing are not enough to cover investment needs, joint stock companies can resort to such an option as additional issue of securities.
The enterprise's own resources mean the totality of material assets owned by the organization. Moreover, both own and borrowed funds are considered as assets.
Sources of formation
The main source of the enterprise's own resources includes those received as a result of the sale of products or the provision of services. This category includes funds from primary and additional activities. Other sources include:
- depreciation deductions;
- the amount from the sale of property owned by the enterprise;
- targeted revenues from higher organizations, as well as from the state in the form of subsidies;
- contributions from company founders;
- proceeds from the sale of securities defined as valuable;
- borrowed funds;
- payment of insurance compensation.
Own resources: structure
The financial resources of the organization consist of:
- authorized capital. At its core, it is the start-up capital of the company, formed through monetary contributions from its founders;
- additional, which actually acts as an addition to the statutory one. It is formed at the expense of the amount of additional assessment of the enterprise’s property, the standard period of use of which exceeds one year;
- reserve, used to cover losses, to repurchase one’s securities if the profit received is not enough for this;
- , that is, the monetary resources remaining after the payment of fees and dividends. In most cases, it is directed to development or companies.
 The enterprise's own resources are formed based on:
The enterprise's own resources are formed based on:
- Economic independence. This principle is manifested in the organization’s independent determination of the sources of its income, the direction of spending and investing funds.
- Self-financing, which means covering all costs from the resources of the company itself. And if there are not enough of them, then it is permissible to use borrowed funds.
- Material interest. This principle is implemented through the profit received by the company.
- Responsibility, providing for a system of obligations depending on the results of activities. This principle is implemented through the financial responsibility of the enterprise/company in the form of various fines and penalties.
- Formation of financial reserves, since any commercial activity is associated with risk.
Stay up to date with all the important events of United Traders - subscribe to our