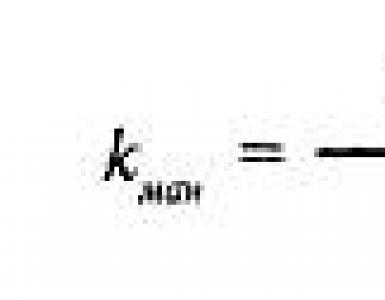Internal sources of financial resources. Sources of enterprise financing
Own sources of financial resources include:
1) authorized capital;
2) depreciation;
3) profit;
4) reserve fund;
5) repair fund;
6) insurance reserves and other sources.
TO own sources of financial resources of an enterprise includes: authorized capital, funds accumulated by the enterprise in the course of its activities, other contributions from individuals and legal entities.
Authorized capital(fund) - the minimum amount of the enterprise’s property, which is formed at the time of creation of the enterprise; determines the right of enterprise participants to exercise management and distribute profits; guarantees repayment of debts to creditors; is the financial basis for the functioning of the enterprise.
The authorized capital is formed at the time of establishment of the enterprise.
The formation of authorized capital is associated with the peculiarities of organizational and legal forms of business: for unitary enterprises - authorized capital, for partnerships - share capital, for companies with additional liability - authorized capital, for joint-stock companies - share capital, for production cooperatives - mutual fund.
The authorized capital of an enterprise is the amount of funds of the founders to ensure statutory activities; it can be formed from cash and other assets (securities, land, transport, intellectual property, etc.), the assessment of which is carried out by the participants of the created enterprise themselves.
For each organizational and legal form, the law establishes a certain amount of the authorized capital at the time of registration and the timing of the formation of the authorized capital.
At state unitary enterprises, the authorized capital is the value of the property assigned by the state to the enterprise with the rights of full economic management; for limited liability companies - the sum of shares of owners, etc., in joint stock companies - the nominal value of shares,
Contributions of founders to the authorized capital can be in the form of cash, property and intangible assets.
When creating partnerships, limited and additional liability companies, the authorized capital is formed at the time of registration in the amount of 50%, the rest during the year.
When creating a joint-stock company and a unitary enterprise at the time of registration, the authorized capital is formed in the amount of 100%.
At the time of registration of a production cooperative, the authorized capital can be formed in the amount of 10% of its value.
The authorized capital must be formed in full within a year.
Sources for increasing the authorized capital can be: external and internal investments, amounts of revaluation of assets, balances of consumption and accumulation funds.
When adjusting the authorized capital, re-registration of the constituent documents is required.
An integral part of the enterprise's equity capital is Extra capital, which has different sources of formation:
Share premium, that is, funds received by the issuer joint-stock company when selling shares in excess of their nominal value;
Amounts received as a result of revaluation of production fixed assets and intangible assets at market value;
Exchange differences associated with the formation of authorized capital in foreign currency. They represent the difference between the assessment of the founder’s debt for the contribution to the authorized capital on the date of receipt of the contribution amount and the ruble assessment of this contribution in the constituent documents.
TO funds accumulated by the enterprise in the course of its activities, include reserve fund, insurance funds, retained earnings (capitalized and consumed)
Reserve capital– part of the accumulated capital of the enterprise. It is formed in accordance with the procedure established by law and has a strictly intended purpose. In particular, the legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the mandatory creation of reserve funds in joint-stock companies. Reserve capital funds are intended to cover losses, repay the company's bonds, and repurchase own shares in the absence of other funds.
retained earnings- part of the accumulated capital of an organization (firm), accumulating profit not paid in the form of dividends, which is an internal source of financial resources of the enterprise.
Enterprises can receive funds for the implementation of targeted activities from higher organizations, individuals, as well as from budgets. Budget assistance can be provided in the form of subventions and subsidies. Subvention– budget funds provided to an enterprise on a free and irrevocable basis for the implementation of certain targeted expenses. Subsidy– budget funds provided to an enterprise on the basis of shared financing of targeted expenses; these funds are part of the enterprise’s own capital.
Thus, equity- part of the value of the enterprise's assets that goes to its owners after satisfying the claims of third parties. The assessment of equity capital can be carried out formally (according to current accounting and reporting data, or according to market estimates) or actually - in the event of liquidation of the enterprise.
TO borrowed sources of formation of financial resources include financial and commodity loans; issue of bonds and other securities; internal accounts payable; amounts received on bail; temporary financial assistance.
Financial loans include bank loans and financial leasing. Bank credit resources- These are loans in cash on the terms of repayment with payment of interest. Long-term loans are used, as a rule, to purchase fixed assets. Short-term loans are used when there is a lack of own working capital to pay for purchased material assets, pay wages, transfer tax payments and other current expenses of the enterprise.
An enterprise can obtain resources by issuing bonds. Bonds is a type of security issued as debt.
Commodity (commercial) loan may be provided in the form of a short-term deferred payment or in the form of a long-term deferred payment with the execution of a bill of exchange.
Domestic accounts payable represents arrears of wages and wage accruals, minimum arrears of taxes and fees, etc.
According to the balance sheet borrowedcapital- monetary valuation of funds provided to the enterprise on a long-term basis by third parties. Borrowed capital is subject to return on the terms that are agreed upon at the time of its mobilization; the amount of borrowed capital reflected in the balance sheet does not change over time.
Formally, borrowed capital is presented in the liabilities side of the balance sheet as a set of long-term liabilities of the enterprise to third parties.
The financial resources of an organization (enterprise) are the totality of its own cash income in cash and non-cash form and income from outside (raised and borrowed), accumulated by the organization (enterprise) and intended to fulfill financial obligations, finance current costs and costs associated with the development of production.
It is worth highlighting the concept “ capital" - part of the financial resources invested in production and generating income upon completion of the turnover. In other words, capital is a transformed form of financial resources.
By source of education financial resources are divided into own(internal) and attracted on different conditions (external), mobilized in the financial market and received through redistribution.
The main share in its own financial resources is profit, which remains at the disposal of the organization (enterprise) and is distributed by decision of the governing bodies. Depending on the financial policy of the organization (enterprise), the profit remaining at its disposal can be used as follows:
- aimed at consumption in full;
- fully invested in other projects not related to the organization’s activities;
- reinvested in the development of the organization in full;
- distributed in the first three directions.
Obviously, the last option is the most preferable; it is only important to observe economically justified proportions of its distribution.
The second most important source of own financial resources are depreciation deductions- monetary expression of the cost of depreciation of fixed production assets and intangible assets. They have a dual nature, since they are included in the costs of production and then, as part of the proceeds from the sale of products, go to the company’s current account, becoming an internal source of financing for both simple and expanded reproduction.
Accumulated depreciation charges form a depreciation fund intended for the reproduction of worn-out fixed assets.
Not all profits remain at the disposal of the organization (enterprise); part of it in the form of taxes and other obligatory payments goes to the budget system. The profit remaining at the disposal of the organization (enterprise) is distributed by decision of the governing bodies for the purposes of accumulation and consumption and reserves. Profit allocated for accumulation is used for the development of production and contributes to the growth of the enterprise's property. Profits allocated for consumption are used to solve social problems.
Attracted, or external, sources of financial resources can be divided into own, borrowed, redistributed and budgetary allocations. This division is determined by the form of capital investment. In the capital market, there are two options for raising funds: equity and debt financing. With equity financing, the company issues and places its shares on the stock market. The second option involves the issue and placement of bonds (fixed-term securities), i.e. provision of capital on the basis of a bond issue. If external investors invest money as entrepreneurial capital, then the result of such an investment is the formation of attracted own financial resources.
Entrepreneurial capital represents capital invested in the authorized capital of another organization (enterprise) for the purpose of making a profit or participating in the management of the organization (enterprise).
Loan capital is transferred to an organization (enterprise) for temporary use on the terms of payment and repayment in the form of bank loans issued for different periods, funds from other organizations (enterprises) in the form of bills of exchange, bond loans.
Funds raised in the financial market include funds from the sale of own shares and bonds, as well as other types of securities.
Funds received through redistribution include insurance compensation for risks incurred, financial resources coming from concerns, associations, parent companies, dividends and interest on securities of other issuers, and budget subsidies.
Budget allocations can be used both on a non-refundable and repayable basis. As a rule, they are allocated to finance government orders, individual investment programs, or as short-term government support for organizations (enterprises) whose products are of national importance.
Financial resources are used by an organization (enterprise) in the process of production and investment activities. They are in constant motion and are in monetary form only in the form of cash balances in a current account in a commercial bank and in the cash desk of an organization (enterprise).
Taking care of financial stability and a stable place in the market economy, the organization (enterprise) distributes its financial resources by type of activity and over time. The deepening of these processes in a modern market economy leads to the complication of financial work and the use of special financial instruments in practice.
The budget of an enterprise at the initial stage of development is formed from the funds of its founders. At the same time, the company’s internal funds at a certain point are no longer sufficient to carry out daily activities, development and work for the future. Sources of external financing make it possible to solve this problem with the least temporary losses.There are two options for external financing. For many companies and individuals with free capital, the optimal way to increase it is to finance various projects instead of organizing a new line of business. Compared to creating your own company, investing in an already existing and successfully operating organization provides greater guarantees of a return of funds with a profit. An additional advantage is the possibility of repurchasing part of the shares.
The second way to attract external sources of financing is to obtain funds from a banking organization. A loan or credit is issued at interest, and financing terms may vary. In most cases, the company makes monthly payments that include interest on the loan and part of the principal.
Options for obtaining external financial resources
The company can attract external financing from banks and other organizations. At the same time, management must calculate all the risks associated with its obligations.To attract external financial resources, companies may issue shares or other securities. As a result, the organization receives funds at its disposal by transferring to individuals and legal entities its debt obligations or shares in the capital of the company. This method of raising funds is called direct financing. Indirect financing involves obtaining loans and advances from a bank.
There can be several sources of external financial resources:
- Cash funds of parent organizations for which the company is a subsidiary. This financing option is often used in large holdings and corporations.
- In some cases, it is possible to raise funds from government sources. Grants and subsidies are designed to improve the financial position of organizations in the existence and successful functioning of which the authorities are interested.
- The volume of foreign investment is growing every year. Foreign companies invest in the development of companies in various industries.
- Raising funds from Russian private companies and individuals is the main source of external financing, along with loans from banking organizations.
Introduction
Management of enterprise financial resources
4 Formation and use of financial resources at micro and macro levels
Conclusion
Bibliography
Introduction
Financial resources are funds of funds at the disposal of the state, economic entities and the population, formed in the process of distribution and redistribution of part of the value of the gross domestic product (GDP), mainly net income in cash, and intended to ensure expanded reproduction and national needs .
The main condition for the growth of financial resources is an increase in national income. Finance and financial resources are not identical concepts. Financial resources in themselves do not determine the essence of finance, do not reveal their internal content and social purpose. Financial science studies not resources as such, but social relations that arise on the basis of the formation, distribution and use of resources; it explores the patterns of development of financial relations.
Although finance belongs to the basic category, it largely depends on the financial policies pursued by governments.
Finance is, first of all, a distribution category. With their help, secondary distribution or redistribution of national income is carried out.
Increasing the effectiveness of the influence of the financial strategy on the sustainable development of the enterprise, built on the regulation of business processes based on balanced scorecards, is carried out through the harmonization of interests in the external and internal environment of the enterprise. This presupposes a corresponding reorientation of the financial strategy during its formation.
The purpose of this work is to consider the financial resources of the enterprise and the sources of their formation. The purpose of the work determines its tasks:
consideration of the principles and features of the organization of enterprise finance;
analysis of the composition and structure of financial resources of enterprises;
characteristics of enterprises’ own sources of financing;
characteristics of borrowed sources of financing for enterprises.
Due to the relevance of this topic, the degree of its development in the domestic scientific and educational literature is quite high. You can find a lot of literature from domestic scientists who pay attention to this issue.
1.Financial resources of the enterprise
The main link of the economy in market economic conditions are enterprises that act as economic entities. To carry out economic activities, obtain products, income and savings, they use certain types of resources: material, labor, financial, and cash.
Among the economic categories mentioned above, the most complex is the category “Financial Resources”. There is still no generally accepted point of view among academic economists about the essence of this category. However, many economists believe that “financial resources” are the funds available to enterprises.
However, money is an independent economic category. The funds of enterprises located in accounts at bank institutions, cash desks, etc. are invested in their concept. They are taken into account in the active accounts of enterprises and are reflected in the assets of their balance sheet.
Financial resources are sources of funds for enterprises, directed towards the formation of their assets. These sources can be our own, borrowed or attracted. They are reflected in the corresponding liability sections of the balance sheet.
Consequently, the financial resources of enterprises are their own, borrowed and attracted monetary capital, which is used by enterprises to form their assets and carry out production and financial activities in order to obtain appropriate income and profit.
The formation of financial resources is carried out in the process of creating enterprises and implementing their financial relations in the implementation of economic and financial activities.
When creating enterprises, the sources of financial resources depend on the form of ownership on the basis of which the enterprise is created. Thus, when creating state-owned enterprises, financial resources are formed from the budget, funds from higher management bodies, funds from other similar enterprises during their reorganization, etc. When creating collective enterprises, they are formed from share (share) contributions of the founders, voluntary contributions from legal entities and individuals persons, etc. All these contributions (funds) represent the authorized (initial) capital and are accumulated in the authorized capital of the created enterprise.
Consequently, the authorized capital is the total value of assets recorded in the constituent documents, which are contributions of owners to the capital of the enterprise. The authorized capital is the main part of the equity capital and the main source of the enterprise's own financial resources. At the expense of its funds, fixed assets and current assets of enterprises are formed.
In the process of further work, the financial resources of enterprises can be replenished from additionally created own sources, attracted and borrowed funds. At the same time, the additionally generated own financial resources (equity capital) include: reserve capital, additional invested capital, other additional capital, retained earnings, targeted financing, etc.
Reserve capital is the amount of reserves created from the retained earnings of the enterprise in accordance with current legislation or constituent documents.
Additional invested capital is the amount of excess of the sale price of shares issued by a joint-stock company over their par value.
Other additional capital - the amount of additional valuation of non-current assets; the value of assets received free of charge by the enterprise from other legal entities or individuals, and other types of additional capital.
Retained earnings are the amount of profit remaining in the enterprise and reinvested in its business activities.
Targeted financing is the amount of targeted revenues received from the budget.
Thus, the authorized capital and additional sources of financing (financial resources) additionally formed during the operation of the enterprise form its own capital.
In addition to equity capital, the financial resources of enterprises are formed from attracted and borrowed sources.
The attracted financial resources include accounts payable for goods, works, services, as well as all types of current liabilities of the enterprise according to calculations:
the amount of advances received from legal entities and individuals for subsequent deliveries of products, performance of work, provision of services;
the amount of debt of the enterprise for all types of payments to the budget, including taxes withheld from employee income;
arrears of contributions to extra-budgetary funds (to the social insurance fund, to the Pension Fund, the Fund for insurance of enterprise property and individual insurance of its employees);
the enterprise's debt to pay dividends to its founders;
the amount of bills issued by the enterprise to suppliers and contractors to ensure the supply of products, performance of work, provision of services, etc.
Borrowed financial resources include long-term and short-term bank loans, as well as other long-term financial obligations associated with raising borrowed funds (except for bank loans), on which interest is charged, etc.
Own, borrowed and attracted capital, which forms, on the one hand, the financial resources of the enterprise and takes part in the financing of their assets, on the other hand, it represents obligations (long-term and short-term) to specific owners - the state, legal entities and individuals.
The composition of financial resources and their volumes depend on the type and size of the enterprise, the type of its activity, and the volume of production. At the same time, the volume of financial resources is closely related to the volume of production and the effective operation of the enterprise. The greater the production volume and the higher the efficiency of the enterprise, the greater the amount of its own financial resources, and vice versa.
The availability of sufficient financial resources and their effective use predetermine the good financial position of the enterprise, solvency, financial stability, and liquidity. In this regard, the most important task of enterprises is to find reserves for increasing their own financial resources and their most effective use in order to improve the efficiency of the enterprise as a whole.
2. Management of enterprise financial resources
1 Centralized and decentralized financial resources
The basis of the financial system is decentralized finance (representing the macro level), since it is in this area that the predominant share of financial resources is formed. Part of these resources is redistributed in accordance with the norms of financial law and budget revenues of all levels and to extra-budgetary funds. At the same time, a significant part of these funds is subsequently used to finance budgetary organizations; commercial organizations in the form of subventions, subsidies, and is also returned to the population in the form of social transfers (pensions, benefits, scholarships, etc.).
Of particular importance in the system of differentiated finance and in the entire financial system of developed countries of the world are the finances of financial intermediaries, which are understood as firms that specialize in organizing the interaction of persons who temporarily have funds with persons in need of funds. Huge financial resources are concentrated in this part of the financial system in the developed countries of the world, used primarily for investment purposes.
Among decentralized finance, the key place belongs to the finance of commercial organizations. Here material wealth is created, goods are produced, services are provided, and profit is generated, which is the main source of production and social development of society.
Household finances play a significant role both in the formation of centralized finance through tax payments and in the formation of the country's effective demand. The higher the income of the population, the higher its demand for various types of material and intangible goods and the greater the opportunities for the development of the economy and social sphere.
Centralized finance is represented by the budget system, as well as state and municipal credit.
In the Budget Code of the Russian Federation, the budget system is defined as a set of budgets at all levels and budgets of state extra-budgetary funds, which is regulated by legal norms and is based on economic relations. The financial resources of the budget system are state property or the property of local government (municipal property). The functioning of the Russian budget system is regulated by the Budget Code of the Russian Federation.
State and municipal loans are distinguished as an independent link in the system of state and municipal finance. State and municipal loans represent monetary relations between the state, municipalities, on behalf of which are the executive authorities of the federal level, the level of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, local governments, on the one hand, and legal entities, individuals, foreign states, international financial organizations, with the other party, regarding obtaining loans, providing credit or guarantees.
State municipal loans are funds raised from individuals, legal entities, foreign states, international financial organizations, under which debt obligations of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities arise as borrowers or guarantors. State and municipal executive authorities of the Russian Federation primarily act as borrowers and guarantors. If granting a loan or receiving a loan immediately affects the amount of financial resources of centralized funds, then the guarantee leads to their change only if the borrower fails to fulfill its obligations on time. State municipal loans are carried out through the issue and placement of securities, obtaining loans from specialized financial and credit institutions and in foreign countries.
2 Sources of formation of financial resources of the enterprise
The sources of formation of financial resources are a set of sources to satisfy the additional need for capital for the coming period, ensuring the development of the enterprise.
In principle, all sources of financial resources of an enterprise can be represented in the following sequence:
own financial resources and on-farm reserves,
· borrowed funds,
·raised financial resources.
Own and attracted sources of financing form the equity capital of the enterprise. Amounts raised from outside sources through these sources are generally non-refundable. Investors participate in the income from the sale of investments on the basis of shared ownership. Borrowed sources of financing form the borrowed capital of the enterprise.
First of all, the company focuses on the use of internal sources of financing.
Own internal funds include:
·authorized capital,
·Extra capital,
· retained earnings.
The organization of authorized capital, its effective use, and management is one of the main and most important tasks of the financial service of an enterprise. Authorized capital is the main source of the enterprise's own funds. The amount of the authorized capital of a joint-stock company reflects the amount of shares issued by it, and of a state and municipal enterprise - the amount of the authorized capital. The authorized capital is changed by the enterprise, as a rule, based on the results of its work for the year after making changes to the constituent documents. You can increase (decrease) the authorized capital by issuing additional shares (or withdrawing a certain number of them from circulation), as well as by increasing (decreasing) the par value of old shares.
Additional capital includes:
·results of revaluation of fixed assets;
· share premium of the joint-stock company;
· monetary and material assets received free of charge for production purposes;
·budget allocations to finance capital investments;
· funds to replenish working capital.
Retained profit is profit received in a certain period and not directed during its distribution for consumption by owners and staff. This part of the profit is intended for capitalization, i.e. for reinvestment in production. In its economic content, it is one of the forms of reserve of the enterprise’s own financial resources, ensuring its production development in the coming period.
Raised funds of enterprises are funds provided on an ongoing basis, for which income can be paid to the owners of these funds, and which may not be returned to the owners. These include: funds received from the placement of shares of a joint-stock company; shares and other contributions of members of labor collectives, citizens, legal entities to the authorized capital of the enterprise; funds allocated by higher holding and joint-stock companies, government funds provided for targeted investment in the form of subsidies, grants and equity participation; funds of foreign investors in the form of participation in the authorized capital of joint ventures and direct investments of international organizations, states, individuals and legal entities.
To cover the need for fixed and working capital, in some cases it becomes necessary for an enterprise to attract borrowed capital. Such a need may arise for reasons beyond the control of the enterprise. They may be the optionality of partners, emergency circumstances, reconstruction and technical re-equipment of production, lack of sufficient start-up capital, seasonality in production, procurement, processing, supply and sales of products and other reasons.
Thus, borrowed capital, borrowed financial resources are funds and other property raised to finance the development of an enterprise on a repayable basis. The main types of borrowed capital are: bank loan, financial leasing, commodity (commercial) loan, bond issue and others.
Borrowed capital over the period is divided into:
short;
long-term.
As a rule, borrowed capital for a period of up to one year is classified as short-term, and more than a year is classified as long-term. The question of how to finance certain assets of an enterprise - through short-term or long-term capital - must be discussed in each specific case. The efficiency of investing borrowed capital is determined by the degree of return on fixed or working capital.
According to sources of financing, borrowed capital is divided into:
Bank loan;
placement of bonds;
loans to legal entities against debt obligations;
Long-term bank loans, bond placements and corporate loans are traditional instruments of debt financing. Bank loans are provided to an enterprise on the basis of a loan agreement, the loan is provided on the terms of payment, urgency, repayment against collateral: guarantees, real estate pledge, pledge of other assets of the enterprise. Many enterprises, regardless of their form of ownership, are created with very limited capital. This practically does not allow them to fully carry out statutory activities at their own expense and leads to their involvement in the turnover of significant credit resources. Not only large investment projects are credited, but also costs for current activities: reconstruction, expansion, reorganization of production facilities, purchase of leased property by the team and other events.
3 Policy for the formation of own financial resources
The financial basis of the enterprise is the equity capital formed by it.
Authorized fund. It characterizes the initial amount of the enterprise's equity capital invested in the formation of its assets to begin business activities. Its size is determined (declared) by the charter of the enterprise. For enterprises in certain areas of activity and organizational and legal forms (joint stock company, limited liability company), the minimum size of the authorized capital is regulated by law.
Reserve fund (reserve capital). It represents a reserved part of the enterprise's own capital, intended for internal insurance of its economic activities. The size of this reserve part of equity capital is determined by the constituent documents. The formation of a reserve fund (reserve capital) is carried out at the expense of the enterprise’s profits (the minimum amount of profit contributions to the reserve fund is regulated by law).
Special (target) financial funds. These include purposefully formed funds of own financial resources for the purpose of their subsequent targeted spending. These financial funds usually include a depreciation fund, a repair fund, a labor protection fund, a special programs fund, a production development fund and others. The procedure for the formation and use of funds from these funds is regulated by the charter and other constituent and internal documents of the enterprise.
Retained earnings. It characterizes the part of the enterprise’s profit received in the previous period and not used for consumption by the owners (shareholders, shareholders) and staff. This part of the profit is intended for capitalization, i.e. for reinvestment in production development. In terms of its economic content, it is one of the forms of reserve of the enterprise’s own financial resources, ensuring its production development in the coming period.
Other forms of equity. These include settlements for property (when leasing it), settlements with participants (for payment of income to them in the form of interest or dividends) and some others, reflected in the first section of the liability side of the balance sheet.
Managing your own capital is associated not only with ensuring the effective use of the already accumulated part of it, but also with the formation of your own financial resources that ensure the future development of the enterprise. In the process of managing the formation of one’s own financial resources, they are classified according to the sources of this formation.
As part of the internal sources of formation of its own financial resources, the main place belongs to the profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise - it forms the predominant part of its own financial resources, ensures an increase in equity capital, and, accordingly, an increase in the market value of the enterprise. Depreciation charges also play a certain role in the composition of internal sources, especially in enterprises with a high cost of their own fixed assets and intangible assets; however, they do not increase the amount of the enterprise’s own capital, but are only a means of reinvesting it. Other internal sources do not play a significant role in the formation of the enterprise's own financial resources.
As part of the external sources of formation of its own financial resources, the main place belongs to the attraction by the enterprise of additional share (through additional contributions of funds to the authorized capital or joint-stock (through additional issue and sale of shares) capital. For individual enterprises, one of the external sources of formation of their own financial resources may be the gratuitous financial assistance (as a rule, such assistance is provided only to individual state-owned enterprises at different levels.) Other external sources include tangible and intangible assets transferred free of charge to the enterprise and included in its balance sheet.
The basis for managing an enterprise's own capital is managing the formation of its own financial resources. In order to ensure effective management of this process, the enterprise usually develops a special financial policy aimed at attracting its own financial resources from various sources in accordance with the needs of its development in the coming period. The policy of forming its own financial resources is part of the overall financial strategy of the enterprise, which consists in ensuring the necessary level of self-financing of its production development.
The development of a policy for the formation of an enterprise’s own financial resources is carried out according to the following main stages:
Analysis of the formation of the enterprise's own financial resources in the previous period. The purpose of this analysis is to identify the potential for the formation of own financial resources and its compliance with the pace of development of the enterprise.
At the first stage of the analysis, the total volume of formation of own financial resources, the correspondence of the growth rate of own capital with the growth rate of assets and the volume of sold products of the enterprise, the dynamics of the share of own resources in the total volume of formation of financial resources in the pre-plan period are studied.
At the second stage of the analysis, the sources of formation of own financial resources are considered. First of all, the ratio of external and internal sources of formation of own financial resources is studied, as well as the cost of attracting equity capital from various sources.
At the third stage of the analysis, the adequacy of the company's own financial resources generated in the pre-planning period is assessed. The criterion for such an assessment is the indicator “self-financing coefficient of enterprise development”. Its dynamics reflect the tendency for the development of the enterprise to be provided with its own financial resources.
Estimation of the cost of raising equity capital from various sources. This assessment is carried out in the context of the main elements of equity capital formed from internal and external sources. The results of such an assessment serve as the basis for the development of management decisions regarding the selection of alternative sources for the formation of its own financial resources, ensuring an increase in the enterprise’s own capital.
Ensuring the maximum volume of attraction of own financial resources from internal sources. Before turning to external sources for the formation of one’s own financial resources, all possibilities for their formation from internal sources must be realized. Since the main planned internal sources for the formation of the enterprise’s own financial resources are the amount of net profit and depreciation charges, then first of all, in the process of planning these indicators, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of their growth at the expense of various reserves.
The method of accelerated depreciation of the active part of fixed assets increases the possibility of generating one’s own financial resources from this source. However, it should be borne in mind that an increase in the amount of depreciation charges in the process of accelerated depreciation of certain types of fixed assets leads to a corresponding decrease in the amount of net profit.
Ensuring the required volume of attracting own financial resources from external sources. The volume of attraction of own financial resources from external sources is intended to ensure that part of them that could not be formed through internal sources of financing. If the amount of own financial resources attracted from internal sources fully meets the total need for them in the planning period, then there is no need to attract these resources from external sources.
Ensuring that the need for own financial resources is met from external sources is planned by attracting additional share capital (owners or other investors), additional issue of shares or through other sources.
Optimization of the ratio of internal and external sources of formation of own financial resources. This optimization process is based on the following criteria:
a) ensuring the minimum total cost of attracting own financial resources. If the cost of attracting your own financial resources from external sources exceeds the planned cost of raising borrowed funds, then such formation of your own resources should be abandoned;
b) ensuring that the management of the enterprise is maintained by its original founders. The growth of additional share or share capital at the expense of third-party investors may lead to a loss of such controllability.
The effectiveness of the developed policy for the formation of own financial resources is assessed using the coefficient of self-financing of enterprise development in the coming period. Its level must correspond to the goal.
The successful implementation of the developed policy for the formation of one’s own financial resources is associated with the solution of the following main tasks:
carrying out an objective assessment of the value of individual elements of equity capital;
ensuring maximization of the enterprise’s profit generation, taking into account the acceptable level of financial risk;
formation of an effective profit distribution policy (dividend policy) of the enterprise;
formation and effective implementation of a policy of additional issue of shares (emission policy) or attraction of additional share capital.
borrowed dividend current asset
2.4 Formation and use of financial resources at the micro and macro levels
Net income as part of the gross domestic product (GDP) is the main source of financial resources. Based on the distribution and redistribution of part of GDP, centralized and decentralized funds of funds are created.
Part of the net income is directed to the expanded reproduction of the sphere of material production to create decentralized financial resources that are at the disposal of economic entities (enterprises, associations, organizations), i.e. are formed at the micro level and are used for production expansion costs. Funds created from decentralized financial resources are used for new capital investments, increasing working capital, financing scientific and technological progress, carrying out environmental protection measures, etc. The implementation of these costs through the use of decentralized financial resources makes it possible to provide funds for the reproduction process of elements of social labor and their expanded reproduction.
At the same time, decentralized financial resources generated from part of net income are a source of expanded reproduction of the second element of the total social product - the cost of labor. Targeted funds created using decentralized financial resources are used to provide social amenities for workers, additional material incentives, etc.
The second largest source of formation of decentralized financial resources - depreciation charges - is formed at the expense of the cost of fixed production assets. Taking into account the long-term nature of the replacement of worn-out fixed assets, depreciation charges, unlike other elements of financial resources, have to a greater extent the functions of replenishment and replacement, but since the replacement of worn-out fixed assets occurs over a long period, their replacement occurs on a fundamentally new technical basis ( the depreciation fund does not act as a source of simple reproduction, since simple replacement on the previous technical and technological basis is meaningless).
Depreciation charges, together with another main source, part of net income, become an important source of expanded reproduction. These funds are used for new construction, reconstruction, expansion and modernization of existing fixed assets, acquisition of more productive equipment and modern technologies, which corresponds to the established practice of using depreciation fund funds. As a result of the long-term nature of the replacement of fixed assets, there is a gap between the initial cost of fixed assets that ensure reproduction and their material content. The depreciation fund becomes an independent target source of financing capital investments on an expanded basis. Of course, in conditions of inflation, the nature of financing the entire reproduction process changes.
Sources for the formation of decentralized financial resources are also savings from reducing the cost of construction and installation work performed by households. way; mobilization of internal resources in construction; increase in sustainable liabilities; proceeds from the sale of retired and surplus property, etc.
The vast majority of Russian enterprises rely on funding from the state budget. Firstly, this is the most traditional source of funding, and, therefore, trying to obtain funding from the regional administration or government is more common and does not require new knowledge and skills from management. Secondly, preparing a project for a private investor is much more difficult than for the state: the state’s requirements for disclosing information and preparing investment projects are more formal than professional. Thirdly, the state is the most loyal creditor, and many enterprises do not repay loans received from it on time without fear of being declared bankrupt.
Borrowed and attracted funds (bank loans, accounts payable, funds received from the issue of shares, transactions with other securities, etc.) participate in the formation of decentralized financial resources. The implementation of the listed costs through the use of decentralized financial resources makes it possible to provide funds for the process of expanded reproduction at the micro level. This procedure for carrying out the reproduction process is objective and independent of forms of ownership.
The other part of net income, in accordance with the essence of finance, is the main source of the formation of centralized financial resources, which are the basis for the financial provision of national needs, reflecting the macroeconomic level.
If decentralized financial resources are the main form of ensuring the expanded reproduction of direct economic entities, then centralized financial resources are the result of the redistribution of mainly net income through tax and non-tax payments and deductions. It is the growth of net income in its main form of expression - profit - that determines high or low growth rates of financial resources.
Sources for the formation of centralized funds of financial resources are also contributions from business entities to state social insurance, property and personal insurance, to various extra-budgetary funds (social protection fund, road fund, employment fund, etc.).
Centralized financial resources are also formed at the expense of part of the national wealth involved in economic circulation (from the sale of the country’s gold reserves, energy resources, proceeds from foreign economic activity, etc.), as well as through the use of funds received from the sale of government securities, bonds, placements loans, etc.
A small part of centralized financial resources is formed from revenues from the population (taxes, fees, income from loans and lotteries, etc.).
Centralized financial resources through redistribution processes (taxes, deductions, etc.) are concentrated mainly in the state budget, extra-budgetary funds, and the state property and personal insurance fund. Part of the financial resources is created by redistributing the cost of the necessary product in the form of deductions to the state budget from taxes from the population, contributions to the social insurance fund and other cash receipts from the population.
The bulk of financial resources are accumulated in the centralized fund of financial resources of the state - the state budget. The concentration of large funds in the budget contributes to a unified financial policy and ensures the possibility of financing the most important national programs. Financial resources are directed to economic development, financing of socio-cultural events, social protection of the population, pensions, financing of defense and law enforcement agencies, public administration, payment of insurance amounts for all types of property and personal insurance, etc.
Allocation of financial resources
Since the main task of a commercial organization is to maximize profit, the problem of allocating financial resources constantly arises: investments to expand the main activities of a commercial organization or investments in other assets. As is known, the economic significance of profit is associated with obtaining results from investments in the most profitable assets.
The following main directions for the distribution of financial resources of a commercial organization can be distinguished:
Capital investments.
Expansion of working capital.
Carrying out research and development work.
Paying taxes.
Tutoring
Need help studying a topic?
Our specialists will advise or provide tutoring services on topics that interest you.
Submit your application indicating the topic right now to find out about the possibility of obtaining a consultation.
Internal financing involves the use of those financial resources, the sources of which are generated in the process of the financial and economic activities of the organization. Examples of such sources include net profit, depreciation, accounts payable, reserves for future expenses and payments, and deferred income.
At external financing funds coming into the organization from the outside world are used. Sources of external financing can be founders, citizens, the state, financial and credit organizations, and non-financial organizations.
Grouping of financial resources of organizations by sources of their formation is presented in the figure below.

An organization's financial resources, unlike material and labor resources, are interchangeable and susceptible to inflation and devaluation.
Currently, an urgent problem for domestic industrial enterprises is the state of deterioration of which has reached 70%. In this case, we are talking not only about physical, but also about moral wear and tear. There is an urgent need to re-equip Russian enterprises with new high-tech equipment. In this case, the choice of source of financing for this re-equipment is important.
The following sources of funding are distinguished:
- Internal sources of the enterprise(net profit, depreciation, sale or rental of unused assets).
- Involved funds(foreign investment).
- Borrowed funds(, bills).
- Mixed(complex, combined) financing.
Internal sources of financing of the enterprise
Involved funds
When choosing a foreign investor as a source of financing, an enterprise should take into account the fact that the investor is interested in high profits, the company itself and his share of ownership in it. The higher the share of foreign investment, the less control the owner of the enterprise has.
Remains debt financing, in which there is a choice between and . Most often, in practice, the effectiveness of leasing is determined by comparing it with a bank loan, which is not entirely correct, because for each specific transaction one has to take into account its own specific conditions.
Credit - as a source of financing for an enterprise
- a loan in monetary or commodity form provided by the lender to the borrower on the terms of repayment, most often with the borrower paying interest for using the loan. This form of financing is the most common.
Advantages of the loan:
- the credit form of financing is characterized by greater independence in the use of received funds without any special conditions;
- Most often, a loan is offered by a bank that services a specific enterprise, so the process of obtaining a loan becomes very quick.
The disadvantages of the loan include the following:
- the loan term in rare cases exceeds 3 years, which is prohibitive for enterprises aimed at long-term profit;
- To obtain a loan, an enterprise must provide collateral, often equivalent to the amount of the loan itself;
- in some cases, banks offer to open a current account as one of the conditions for bank lending, which is not always beneficial to the enterprise;
- With this form of financing, an enterprise can use a standard depreciation scheme for purchased equipment, which obliges it to pay property taxes throughout the entire period of use.
Leasing - as a source of financing for an enterprise
is a special complex form of entrepreneurial activity that allows one party - the lessee - to effectively update fixed assets, and the other - the lessor - to expand the boundaries of activity on mutually beneficial terms for both parties.
Advantages of leasing:
- Leasing involves 100% lending and does not require you to start payments immediately. When using a conventional loan to purchase property, the company must pay about 15% of the cost from its own funds.
- Leasing allows an enterprise that does not have significant financial resources to begin implementing a large project.
It is much easier for an enterprise to obtain a leasing contract than a loan - after all the equipment itself serves as security for the transaction.
A leasing agreement is more flexible than a loan. A loan always involves limited amounts and repayment terms. When leasing, an enterprise can calculate its income and work out with the lessor an appropriate financing scheme that is convenient for it. Repayment can be made from funds received from the sale of products produced on leased equipment. The company has additional opportunities to expand production capacity: payments under the leasing agreement are distributed over the entire term of the agreement and, thus, additional funds are freed up for investment in other types of assets.
Leasing does not increase debt in the company’s balance sheet and does not affect the ratio of equity and borrowed funds, i.e. does not reduce the enterprise’s ability to obtain additional loans. It is very important that equipment purchased under a leasing agreement may not be listed on the lessee’s balance sheet during the entire term of the agreement, and therefore does not increase assets, which exempts the company from paying taxes on acquired fixed assets.
The Russian Federation has retained the right to choose the balance sheet accounting of property received (transferred) under financial lease on the balance sheet of the lessor or lessee. The initial cost of the property that is the subject of leasing is the amount of the lessor's expenses for its acquisition. In addition, since 2002, regardless of the chosen method of accounting for the property that is the subject of the leasing agreement (on the balance sheet of the lessor or the lessee), lease payments reduce the tax base (Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Article 269 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation introduces a restriction on the amount of interest on loans that the lessor can attribute to reducing the tax base, but in other cases the lessor can attribute the amount of interest on the loan to reducing the tax base.
Leasing payments, paid by the enterprise, entirely attributed to production. If the property received under leasing is accounted for on the balance sheet of the lessee, then the enterprise can receive benefits associated with the possibility of accelerated depreciation of the leased asset. Depreciation charges for such property can be calculated based on its cost and norms approved in the prescribed manner, increased by a factor not exceeding 3.
Leasing companies unlike banks no deposit needed, if the property or equipment is liquid on the secondary market.
Leasing allows an enterprise to minimize taxation on completely legal grounds, as well as to attribute all costs of equipment maintenance to the lessor.