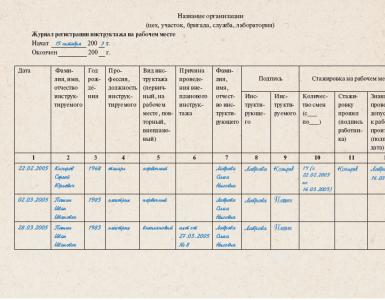
Periodic medical examinations. Medical examinations of employees - the procedure for conducting mandatory, periodic and extraordinary medical examinations What is the organization of medical examinations
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
Procedure for purchasing medicines and pharmaceutical products and pricing
1. Purpose
2. Scope of application
3. Personnel and responsibility
4. Main part. Supplier selection criteria
4.1. Selecting a supplier.
4.2. Procurement of medicines and TAA.
4.3. Processing of received invoices and pricing
5. Literature
1. Purpose
standardization of the procedure for selecting and evaluating suppliers of medicinal products (including thermolabile ones) and other pharmaceutical assortment products (TAA), in accordance with the requirements of good pharmacy practice and good practice of storage and transportation of medicinal products in order to minimize the risks of entering into civil circulation substandard, falsified and counterfeit medicinal products (hereinafter referred to as medicinal products), pharmaceutical products.
Determination of the procedure for purchasing drugs and TAA.
2. Application area
Where: pharmacy
When: In the process of selecting a supplier to work with and purchasing drugs and TAA from suppliers with whom cooperation has been established.
3. Personnel and responsibility
for organizing conditions for meeting the requirements of SOP;
for concluding contracts for the supply of medicines and TAA
Quality Officer:
for the availability of SOPs in pharmacies;
for familiarizing pharmacy managers with SOPs;
for timely bringing SOP into compliance with current regulatory documents;
for conducting internal audits of SOP implementation;
Head of pharmacy organization:
for implementation of SOP
for familiarizing the new employee with SOPs during the adaptation period;
for familiarizing pharmacists and pharmacists with changes to the SOP after bringing the SOP into compliance with the current regulatory documents:
for compliance with SOP requirements;
timely execution of the order for medicines and TAA
Pharmacist, pharmacist;
for maintaining the Defect Logbook
for the timely inclusion of missing or running out of goods in the application.
4. Main part of the SOP
4.1. Selecting a supplier.
In order to provide a pharmacy organization with the necessary range of goods, the Company enters into agreements with suppliers of medicines and TAA, for which the Director Suppliers of pharmaceutical products are assessed, taking into account, among other things, the following criteria:
|
Criterion |
What exactly is being assessed? |
|
a) compliance of the supplier with the requirements of the current legislation of the Russian Federation on licensing of certain types of activities; |
Registration of a supplier as an individual entrepreneur or legal entity Availability of a license for pharmaceutical activities: Storage of medicines Wholesale trade of medicines Transportation of medicines Term of activity of the supplier in the pharmaceutical market If the supplier involves third parties, for example, to transport goods (in compliance with the requirements for the transportation of medicines), there must be properly executed contracts and other necessary documents between the supplier and any third parties. These contracts must clearly establish the liability of third parties. |
|
b) the business reputation of the supplier in the pharmaceutical market, based on the presence of facts of recall of falsified, substandard, counterfeit pharmaceutical products, failure to fulfill accepted contractual obligations, orders of authorized state control bodies on facts of violation of the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation; |
The presence or absence of information about the supplier on the website of Roszdravnadzor or the media as a violator of the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation (and the frequency of appearance of such information) |
|
c) the demand for pharmaceutical products offered by the supplier for further sale, compliance of the quality of pharmaceutical products with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation; |
Studying the supplier’s price list, draft supply agreement |
|
d) compliance by the supplier with the requirements established by these Rules for the preparation of documentation, the availability of a document with a list of declarations of product conformity with established requirements, a protocol for agreeing on prices for medicinal products included in the list of vital and essential medicinal products; |
Availability of relevant clauses in the draft supply agreement: Requirements for accompanying documents Providing quality documents for goods and ease of working with them |
|
e) compliance by the supplier with temperature conditions during transportation of thermolabile drugs, including immunobiological drugs; |
Availability of the type of activity in the license Transportation of medicines |
|
f) provision by the supplier of a quality guarantee for the supplied pharmaceutical products; |
Availability of a corresponding section in the supply agreement |
|
g) competitiveness of the contract terms offered by the supplier; |
The conditions offered by the supplier are assessed with the capabilities of the enterprise |
|
h) economic feasibility of the terms of delivery of goods proposed by the supplier (number of packages supplied, minimum delivery amount); |
The terms of the supply agreement are assessed in comparison with other suppliers |
|
i) the ability to supply a wide range; |
Price list is evaluated |
|
j) compliance of the delivery time with the working time of the retail trade entity. |
Required condition |
|
k) procedure and deadlines for submitting claims regarding quantity and quality |
Mandatory condition of the contract |
|
l) procedure and terms for returning falsified, substandard and counterfeit goods according to letters from the RZN |
Mandatory condition of the contract |
If the above conditions are met, an agreement is concluded with the supplier, taking into account the requirements of the legislation on the fundamentals of state regulation of trading activities in the Russian Federation.
Control of the quantitative and qualitative parameters of purchased pharmaceutical products, as well as the timing of their delivery in accordance with contracts, is carried out by the heads of pharmacy organizations. In case of systematic violation by the supplier of the terms of the supply contract in terms of:
delivery times of ordered goods,
compliance with transportation conditions,
procedure and timing for consideration of timely submitted claims
procedure and terms for returning falsified, substandard and counterfeit goods according to RZN letters
management of LLC "KAFA-PHARM"The reasons for the occurrence of such violations are determined, and based on the results, a decision is made on the advisability of further cooperation with this supplier.
4.2. Procurement of drugs and TAA
Documents used.
|
Defect log book (including electronic) |
|
|
A journal for the provision of medicines included in the minimum range of medicines necessary for the provision of medical care (hereinafter referred to as the minimum range), but not available at the time of the buyer’s request; |
|
|
Register of registered prices for vital and essential drugs |
Ensuring consumer demand for pharmaceutical products is carried out by the enterprise while observing all production processes, but primarily by maintaining an adequate inventory and the required assortment, taking into account the balance between the need and the financial capabilities of the Company.
Determining the need for drugs by nomenclature and quantity when opening a pharmacy is carried out by a pharmaceutical worker who has sufficient experience working in a retail pharmacy (pharmacy chain) in Feodosia, taking into account the location of the pharmacy organization (located in a residential area or in a shopping center), the presence of nearby medical organizations and the profile of these organizations, the population served by the pharmacy organization.
In daily work, purchasing is carried out by the head of the pharmacy organization. The range and quantity of purchased drugs and TAA are adjusted taking into account real needs.
The application is formed on the basis of:
|
Requirements for the availability of a minimum range of medicines established by current legislation |
|
|
Statistical data on sales of pharmaceutical products obtained from the material accounting program; |
|
|
Defect log entries |
|
|
Analysis of seasonality factors in the incidence and consumption of pharmaceutical products (summer, winter) |
|
|
Media analysis. |
The application is generated electronically using software products for automating work with suppliers.
The application is sent as needed, incl. urgently.
Submitted applications are received by an authorized person, who analyzes them, corrects them (if necessary) and sends them directly to suppliers.
4.3. Processing of received invoices and pricing.
Processing and pricing is carried out by a person appointed by order of the director.
The responsibilities of the person responsible for pricing include:
processing of electronic invoices;
control of the identity of electronic invoices coming from suppliers and entering the material accounting program;
formation of retail prices taking into account restrictions on drugs, prices for which are subject to state regulation, control of prices for these drugs
development of annexes to the Protocols for agreeing prices for medicines, the prices of which are subject to state regulation.
List of goods whose prices are subject to state regulation:
1. Vital and essential drugs, the list of which is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation for each year.
2. Baby food.
5. Literature
Civil Code of the Russian Federation
Federal Law of April 12, 2010 No. 61-FZ "On the circulation of medicines"
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 22, 2011 N 1081 (as amended on September 23, 2016) “On licensing of pharmaceutical activities”
Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated August 31, 2016 N 646n “On approval of the Rules for Good Practice for Storage and Transportation of Medicines for Medical Use”
Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated August 31, 2016 N 647n “On approval of the Rules of Good Pharmacy Practice for Medicinal Products for Medical Use”
Resolution of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated February 17, 2016 N 19 “On approval of sanitary and epidemiological rules SP 3.3.2.3332-16 “Conditions for transportation and storage of immunobiological medicinal products”
Order of the State Committee on Prices and Tariffs of the Republic of Crimea dated 08/07/2014. No. 4/1 “On establishing the maximum amounts of wholesale markups and the maximum sizes of retail markups to the actual selling prices established by drug manufacturers for drugs included in the list of vital and essential drugs in the territory of the Republic of Crimea.”
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of August 8, 2009 N 654 “On improving state regulation of prices for medicines included in the list of life-saving drugs” necessary and essential medicines"
Current list of vital and essential drugs
SOP PKU.doc
Standard Operating Procedure:
Work with medicinal products subject to subject-quantitative accounting and medicinal products containing, in addition to small quantities of narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances and their precursors, other pharmacologically active substances
1. Purpose
2. Responsibility
3. Application area
4. Main part of the SOP
5. Rationale and literature
5.1. Rules for the release of drugs subject to PCU. The procedure for preparing prescription forms for drugs.
5.2. Rules for the dispensing of drugs subject to PCU according to the requirements of medical organizations.
5.3. Maintaining records of medications subject to PCU in pharmacy organizations.
5.4. Storage of prescriptions and requirements of health care facilities in pharmacy organizations.
5.5. Prohibition on the supply of drugs subject to PCU.
5.6. Storage of drugs subject to PCU in pharmacies.
5.7. Appendix: Combination medicinal products containing small quantities narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances and their precursors. containing NSAIDs and their precursors.
1. Purpose of the SOP: Designation of Standard Operating Procedures for the rules for the release and registration of operations related to the release of medicines, subject to subject-quantitative accounting (PKU)
2. Responsibility: Director - for issuing orders appointing someone responsible for working with medicines subject to PKU, responsible for maintaining and storing the Logbook of transactions related to the circulation of medicines subject to PKU, responsible for storing the keys to the safe (cabinet).
Pharmacy manager for compliance with SOPs.
Pharmacy employees - for compliance with the rules for the dispensing and storage of drugs subject to PCU;
Quality Assurance Officer for a pharmacy organization - for the development and monitoring of implementation of SOPs;
Pharmaceutical workers - for compliance with SOPs without deviations from the prescribed standards.
3. Application area
4. MAIN PART OF SOP
Justification: By order of Minz Drava of Russia from 04/22/2014 No. 183n "On approval of the list of medicines for medical use, subject to subject-quantitative accounting"new list approvedThe number of medicines subject to subject-quantitative accounting.
Documents used.
The dispensing of medicinal products with anabolic activity, medicinal products subject to subject-quantitative accounting, is carried out by pharmaceutical workers holding positions included in the list of positions of pharmaceutical and medical workers in organizations that are granted the right to dispense narcotic drugs and psychotropic drugs to individuals, approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated September 7, 2016 No. 681n, namely:
head of a pharmacy organization, deputy head of a pharmacy organization
pharmacist, pharmacist-technologist
senior pharmacist
- pharmacist
The list of persons admitted to work with drugs subject to PKU is approved by order of the director.
When a pharmacy visitor applies for a medicinal product (medicine) that is subject to subject-quantitative accounting, the pharmacy employee performs the following actions:
|
Without a prescription |
||
|
Subject to prescription |
Evaluates the correctness of the recipe: |
|
|
The drug was issued on form 107-1/u |
Enter the prescription into the Incorrectly Prescribed Prescription Log Stamp the prescription “Invalid” and return it to the buyer with a recommendation to see a doctor and refill the prescription. Notify the manager. |
|
|
The drug was issued on form 148-1/u-88 |
1. Check the correctness of the prescription and its validity period (in accordance with the Appendix) 2. Announces the availability in the pharmacy of drugs containing the active substance prescribed in the prescription in the appropriate dose and release form, indicating: The cost of one individual package (it is obligatory to provide information about the availability of medicines with a lower price); Countries and manufacturing companies. 3. If the pharmacy visitor agrees to purchase the selected drug(s), the pharmacy employee dispenses the quantity of the drug prescribed in the prescription. 4. When presenting a prescription that exceeds the maximum permissible or recommended amount of a medicinal product for prescribing for one prescription, the pharmacist informs the person who submitted the prescription about this, the head of the relevant medical organization and releases to the specified person the correspondingly established maximum permissible or recommended amount of the medicinal product for prescribing per prescription. one recipe with the appropriate mark in the recipe. 5. Places a mark on the back of the recipe indicating: Names of the pharmacy organization; Trade name, dosage and quantity of the drug dispensed; Last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the pharmaceutical worker who dispensed the medicinal product, and his signature; Dates of release of the drug. Places a stamp on the prescription “The drug is dispensed.” 6. Leaves the recipe in the PKU safe (cabinet) for storage. |
On March 1, 2017, the Rules for Good Pharmacy Practice of Medicines for Medical Use came into force (Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia No. 647n dated 08/31/2016; registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on 01/09/2017 No. 45113). The document establishes requirements for the activities of pharmacy organizations of all forms of ownership, including in the field of the quality management system.
To help you implement a quality management system in a pharmacy organization, we have prepared standard operating procedures within the framework of the requirements of the NAP Rules.
After payment you will have access to the document: SOP “Procedure for hygienic treatment of personnel’s hands.”
What will be in the document?
The standard operating procedure “Personnel Hand Hygiene Procedure” is a text document that reflects:
- hand washing procedure for pharmacy employees;
- procedure for treating the hands of pharmacy employees with a disinfectant.
- Purpose of SOP
- Personnel (for whom the SOP is intended)
- Basic terms and definitions
- Raw materials
- General provisions
- Responsibility and authority for the implementation of the quality management system in the direction of the sanitary regime in the pharmacy organization
- Documentation
- Procedures
- Education
- Literature
- Distribution
- Reference list
An SOP is a standard document that describes standard procedures in a pharmacy organization.
The most common questions regarding the implementation of this document were answered during the webinar by the head of the Department of Licensing and Monitoring Compliance with Mandatory Requirements of Roszdravnadzor Irina Krupnova and the Executive Director of the Non-Profit Partnership “Pharmacy Guild” and the Union “National Chamber of Pharmacy” Elena Nevolina.
Anna Grishunina, LekOboz: What significant changes have occurred with the introduction of the Rules of Good Pharmacy Practice?
“This is primarily a requirement to document standard operating procedures (SOPs) to prevent various violations. The rules of good pharmacy practice require documentation of all major business processes that affect the quality of service delivery. Thanks to this requirement, the influence of the human factor is minimized. Maintaining these records confirms the quality of products and services. SOPs will also help reduce the risk of errors in cases where another person must perform his functions during an employee's vacation or illness. Having familiarized himself with the standard operating procedure, he will very quickly get into the swing of things, and thus the risk of errors will be minimized as much as possible, because the standard organizational procedure will clearly spell out the procedure.
This document cannot be created specifically for inspection authorities and then placed in a distant drawer. You need to work with it every day, make notes in it about what steps are being taken to reduce the number of violations of current legislation. If SOPs are created just for show, then this will definitely come out during inspection. Nobody requires pharmacy workers to create a huge multi-page ledger. It is important to analyze all the main types of work from the point of view of all possible risks and describe how a particular business process should be carried out - acceptance of goods, storage of medicines, dispensing of goods, manufacturing of medicines (if there is a production department) in order to prevent employee errors. And it is imperative to specify in the SOPs who will be responsible
 Current legislation provides for a strict procedure for organizing medical examinations at an enterprise, violation of which may result in the employer being held liable. At the same time, it is also possible to conduct a medical examination on the territory of the enterprise, which can have a sufficient number of advantages for both the employer and the employees. It will be useful for all parties to the labor relationship to know how the medical examination is properly ensured at the enterprise, and how this process is organized.
Current legislation provides for a strict procedure for organizing medical examinations at an enterprise, violation of which may result in the employer being held liable. At the same time, it is also possible to conduct a medical examination on the territory of the enterprise, which can have a sufficient number of advantages for both the employer and the employees. It will be useful for all parties to the labor relationship to know how the medical examination is properly ensured at the enterprise, and how this process is organized.
What is a medical examination at an enterprise and the regulatory framework for conducting it?
By medical examination, Russian legislation implies a mandatory procedure in some cases, which consists of examination by a certain list of medical specialists, as well as passing a number of prescribed tests. At the same time, legislative regulation of this issue is provided by a very wide range of regulations and documents. In particular, both employees and employers who wish to ensure a medical examination at the enterprise should at least pay attention to the provisions of the following regulations:
- Federal Law No. 323 dated November 21, 2011. The standards of this law establish the general principles and definition of a medical examination, the main types of medical examinations and other aspects of the said procedure.
- Federal Law No. 52 dated March 30, 1999. This law considers in its provisions the basic principles by which measures are taken to protect the Russian population from unfavorable sanitary and epidemiological factors. And medical examinations at the enterprise are one of the important components of these protective measures.
- Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 302n dated April 12, 2011. This document contains the most complete list of harmful factors inherent in various professions and activities, and also establishes the relationship between various ones and the need to undergo. Also, depending on each harmful factor, this order regulates not only the regularity of periodic medical examinations at the enterprise, but also the doctors themselves and the tests that must be passed by employees.
- Order of Rospotrebnadzor No. 402 dated May 20, 2005. The regulatory provisions of this document establish the concept, its form, and also regulate the general principles of its design and situations in which employees, in addition to medical examinations at the enterprise, should obtain a medical book.
- Article 69 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The provisions of this article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establish the possibility of conducting medical examinations in relation to certain categories of workers when they do so.
- Article 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The standards of this article of the Labor Code regulate the issues of conducting medical examinations at the enterprise as a whole, and also establish a short list of positions in respect of which this procedure is mandatory and cannot be ignored.
In general, there are a much larger number of regulations governing the conduct of medical examinations by representatives of individual professions or organizations. For example, medical examinations of employees of the prosecutor’s office, the Ministry of Internal Affairs or the FSB are mandatory and are carried out separately - the relevant laws dedicated to each of these structures can inform about the procedure for conducting medical examinations in these situations.
In general, it should be remembered that a medical examination for a number of professions is a mandatory action that must be performed both upon hiring and periodically with some regularity. Violation of the procedure for conducting a medical examination in this case may be grounds for holding the employer liable. But also in relation to the employee, the legislation provides for the possibility of imposing certain sanctions.
Thus, if the employee did not undergo a medical examination through no fault of the employer, then the latter not only has the right, but is also obliged to remove the employee from work duties, without maintaining his salary until the medical examination is completed.
The procedure for conducting medical examinations at the enterprise
There are no direct legislative requirements that would strictly establish the general procedure for conducting medical examinations in simple organizations - such a procedure may be provided for in individual public services and involve, for example, as in the case of the police, the imposition of additional disciplinary sanctions on employees for failure to undergo a medical examination. But in general situations, the employer directly has the right to determine the procedure and methods for conducting a medical examination in an organization.
The main instrument used to establish and consolidate such an order are the local regulations of the enterprise, as well as the provisions of the collective agreement or directly individual labor contracts with employees. At the same time, the employer has the right to establish mandatory medical examinations for employees for whom they are not required from the point of view of current legislation.
However, in any case, compensation for the cost of a medical examination must be provided by the employer in accordance with the provisions of the Labor Code. In general, in practice, several main options for organizing medical examinations at an enterprise are used:
- Referring employees to undergo independent medical examinations at any accredited medical institution. In this case, the employer does not bear any responsibility for the preliminary conclusion of contracts with medical organizations and simply issues each employee a referral to undergo a medical examination. In this case, the employee subsequently has the right to compensation for all costs associated with the medical examination from the employer directly. This method is usually used in small organizations where it is not possible to provide centralized labor protection measures.
- Concluding an agreement on medical care for employees and conducting medical examinations with a separate medical institution. If the organization assumes such a procedure for conducting a medical examination, the employer enters into an agreement with the medical institution to conduct medical examinations. This approach can significantly reduce the overall costs of the employer with a large staff of employees, and also reduces the costs of the employees themselves - with such centralized service, they do not need to confirm the cost of a medical examination, since it was initially paid for by the employer. In addition, in these situations, medical examinations are often completed without any queues or delays in the shortest possible time.
- On-site medical examination. Some medical institutions offer medical examination services directly on the premises of the enterprise. This method allows you to minimize the loss of actual working time for employees to undergo a medical examination, but in itself it is much more costly for the enterprise.
- Organizing your own medical complex. With regard to periodic medical examinations, only accredited medical institutions or organizations that have their own departmental hospitals have the opportunity to organize them directly on the territory of the enterprise. This is due to the fact that there are very many requirements for the qualifications of doctors and the range of tests required for a medical examination, and it is quite difficult to provide such a large staff of medical specialists with all the necessary equipment. However, in the context of daily medical examinations, for example, of drivers or miners, it is enough for an enterprise to have a specially equipped medical office with one accredited employee, which is much easier to do than calling doctors every day to conduct a medical examination, or sending workers to a medical institution.
The immediate procedure for organizing medical examinations may look approximately as follows:
- The employer sets out in the regulations of the enterprise the conditions and principles for medical examinations by employees. In this case, it is recommended to highlight the specification by position, age of employees, their departments and maximize the accuracy of issuing referrals. The employer also appoints a person responsible for labor protection, who may be charged with storing documentation related to the medical examination and maintaining relevant logs.
- The employer establishes the conditions for confirming that employees have undergone a medical examination. They may include both the provision of a medical record for safekeeping, if it is issued for employees, and the provision of only medical examination certificates, or copies of these documents. In addition, the procedure for recording and storing the said documentation is established.
- The person responsible for labor protection draws up a schedule for medical examinations. In this case, there may be two different key approaches. In one case, the person responsible for labor protection keeps records of medical examinations for each individual employee, issuing a referral for him when the next periodic medical examination is due. In another case, the enterprise establishes general schedules for conducting medical examinations for individual departments or generally for all employees of the organization, which can significantly reduce the time and paperwork costs associated with carrying out these procedures.
- If an employee is identified who refuses or for other reasons does not undergo a medical examination on time, the employer must suspend him from performing his job duties, and if the period of suspension exceeds four months, he has the right to dismiss such an employee.
If an employee has not passed a medical examination due to the fault of the employer, then the latter cannot dismiss the said employee, and for the entire period of suspension the employee must retain his average salary.
The employer should take into account many other nuances related to medical examinations. In particular, he can establish the procedure for undergoing medical examinations at strictly designated times and in certain medical institutions. Violation of this procedure by an employee, for example, undergoing a medical examination at the wrong time or in the wrong place, deprives the latter of the right to receive compensation for the medical examination, but does not make its results invalid - the employer is obliged to accept a certificate of medical examination in any case if it is properly executed manner in an accredited institution and in accordance with the list of doctors and tests required to undergo.
Medical examination on the territory of the enterprise - is it possible, how to conduct it
Separately, the possibility of conducting medical examinations at the enterprise should be directly considered. Currently, many medical institutions offer the opportunity to conduct medical examinations and take tests on the territory of the organizations themselves, without actually taking workers away from work for a long time. This approach allows us to minimize the costs associated with the absence of employees from work, and also makes it possible to more effectively control the inspection of all employees without exception.
Despite the fact that the cost of such services for conducting a medical examination on the territory of the organization, this procedure also has a number of advantages that can provide additional savings. So, as mentioned above, the time workers take away from the work process in this case will be minimal. In addition, the employer, in any case, is obliged to ensure the recording and payment of working time spent by employees on undergoing a medical examination - and speeding up the entire procedure can ultimately seriously affect the employer’s costs.
But conducting medical examinations on the territory of the organization is most relevant directly for those areas of activity where employees are required to undergo not only initial or periodic medical examinations, but also daily examinations. So, this applies primarily to drivers and employees involved in underground work. In this case, the employer can either organize his own office and hire a full-time specialist who has the right to conduct medical examinations, or again resort to the services of third-party medical institutions.
They, in turn, can either organize an office for themselves on the territory of the enterprise or use the office offered by the employer, or use other methods of on-site medical examinations. For example, cars with a ready-made office equipped in the back, which has all the necessary equipment for quick and convenient inspections on the territory of any enterprise, are now quite common.
Let us examine in detail the procedure for conducting medical examinations of enterprise employees, taking into account the changes that came into force in 2018.
Read our article:
Medical examinations of enterprise employees in a new way in 2018
A medical examination (MO) is a comprehensive examination of an employee in order to identify negative changes in his health and determine his suitability to perform job duties. First of all, a medical examination is necessary for personnel who are exposed to harmful and hazardous production factors (HAPF) in the workplace. The list of such factors and the procedure for undergoing medical examinations by employees are established by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 12, 2011 No. 302n.
In March 2018, the approved changes came into force. It was expanded (clause 20 of Appendix No. 2): instead of workers of social shelters and nursing homes, workers of social service organizations providing social services must now be sent to the Ministry of Defense:
- in stationary form of social services;
- semi-stationary form of social services;
- in the form of social services at home.
The procedure for conducting a medical examination in Appendix No. 3, as well as the requirements for documents confirming its completion, have not changed.
Article 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - medical examinations
Mandatory medical preliminary and periodic examinations: organization of implementation
As we mentioned above, the procedure for conducting medical examinations is determined by Appendix 3 to Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 302n.
A preliminary medical examination is carried out upon hiring. It allows:
- assess the employee’s ability to perform professional functions without harm to health;
- promptly identify the initial ones and prevent their development.
The algorithm is as follows:
1. The employer issues it to the person applying for work, indicating the position, profession or type of work, as well as a list of those present at the workplace.
2. A person applying for a job submits the following documents to the medical organization:
- direction;
- passport (or other standard identification document);
- decision of the medical commission (in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation).
3. The preliminary inspection is considered passed when:
- the person applying for work was examined by all medical specialists;
- All laboratory and functional studies were performed.
4. After passing the medical organization’s medical examination, which must be signed by the chairman of the medical commission indicating his last name and initials. The document is certified by the seal of a medical organization, which prepares a conclusion in two copies. The first is attached to the outpatient card, the second is given to the person who has undergone a medical examination.
For what purposes are mandatory periodic medical examinations carried out?
Download and use in your work, with which you can quickly determine which employees to send for a periodic medical examination this year, create a list of contingent, a list of names and referrals for a medical examination.
Who should undergo periodic medical examination
The following employees must undergo periodic preventive medical examinations.
- Those exposed to harmful or dangerous production factors, in the presence of which mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations are carried out.
- Performing work specified in the list, during the performance of which mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations of workers are carried out.
- . If these jobs involve persons under 21 years of age, they undergo medical examinations annually (Article 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Involved in underground work. Such employees undergo periodic medical examinations annually (clause 12 of Appendix 2 to Order No. 302n).
- Employed in organizations of the food industry, public catering and trade, water supply facilities, medical organizations and child care institutions (Article 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The frequency of medical examinations for specific professions is given in Appendix No. 2 to Order No. 302n.
- Athletes. They undergo medical examinations annually (Article 348.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Persons under 18 years of age. They undergo medical examinations annually (Article 266 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The List specifies the jobs and professions during which workers must undergo mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations, regardless of what is established at these workplaces and the availability of vocational training.
|
Name of work and professions |
Inspection frequency |
|
1 time per year |
|
|
10. Performed directly on mechanical equipment that has open moving (rotating) structural elements (lathes, milling and other machines, stamping presses, etc.) |
1 time every 2 years |
|
11. Under water, performed by workers in a gas environment under normal pressure conditions |
1 time every 2 years |
|
12. Underground |
1 time per year |
|
13. Performed using insulating and filtering gas masks with a full face part |
1 time every 2 years |
|
14. In food industry organizations, dairy and distribution points, at food product bases and warehouses, where there is contact with food products during their production, storage, sales, including work on sanitary processing and repair of inventory, equipment, as well as work where there is contact with food products during their transportation by all types of transport |
1 time per year |
|
15. In catering organizations, trade, buffets, catering units, including in transport |
1 time per year |
|
16. Performed by students of educational organizations of general and vocational education before and during internship in organizations whose employees are subject to medical examinations |
1 time per year |
|
17. Medical personnel of medical institutions, as well as maternity hospitals (departments), children's hospitals (departments), children's clinics, departments of pathology of newborns, premature babies |
1 time per year |
|
18. In educational organizations of all types and types, as well as children's organizations that do not carry out educational activities (sports sections, creative, leisure children's organizations, etc.) |
1 time per year |
|
19. In children's and adolescent seasonal health organizations |
1 time per year |
|
20. In preschool educational organizations, children's homes, organizations for orphans and children left without parental care (persons in their place), boarding educational organizations, recreational educational organizations, including sanatorium type, children's sanatoriums, year-round recreation camps , as well as social shelters and nursing homes |
1 time per year |
|
21. In consumer service organizations (bathhouse attendants, shower workers, hairdressers) |
1 time per year |
|
22. In swimming pools and spas |
1 time per year |
|
23. In hotels, hostels, passenger carriages (conductors), as a flight attendant |
1 time per year |
|
24. In organizations of the medical industry and pharmacy chains related to the manufacture, packaging and sale of medicines |
1 time per year |
|
25. At water supply facilities related to water treatment and maintenance of water supply networks |
1 time per year |
|
26. Related to milk processing and production of dairy products |
1 time per year |
|
27. On driving land vehicles |
1 time every 2 years |
*If the listed jobs involve persons under 21 years of age, they undergo medical examinations annually (Article 213 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Medical examinations should be carried out already in the presence of harmful or dangerous production factors specified in the list at the workplace, and their level does not matter.
The following factors are exceptions:
- 3.5. - ;
- 3.8., 3.9. - air temperature;
- 3.12. - light environment;
- 4.1. - physical overload;
- 4.4.1., 4.4.2., 4.4.3.- sensory loads.
For these factors, medical examinations are carried out only if working conditions are classified as harmful or dangerous based on the results of the special assessment assessment.
When hiring, for example, accountants, programmers, management personnel and other office employees who spend more than 50 percent of their working time, the employer is obliged to send them for a medical examination (clause 3.2.2.4 of the List of harmful and (or) hazardous production factors approved by Order No. 302n). The frequency of MO is once every two years.
Passing a periodic medical examination
The procedure for conducting periodic medical examinations is regulated by Order No. 302n. The algorithm is as follows:
1. The employer is subject to periodic medical examinations, which indicates:
- name of the employee’s profession or position according to the staffing table;
- name of the harmful production factor.
Then this document is sent within 10 days to the territorial body of Rospotrebnadzor at the actual location of the employer (clause 21 of the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 12, 2011 No. 302n).
2. Based on the approved list of contingent indicating the VOPF, as well as the type of work.
Approved lists are sent to the medical organization. This must be done no later than two months before the start date of the examination agreed with the medical institution. The medical organization, within 10 days from the date of receipt of the name list, draws up a calendar plan for conducting periodic medical examinations.
3. The employer familiarizes employees with the Moscow Region calendar plan. This must be done no later than ten days before the start of the event.
4. The employer provides employees with directions for a medical examination. They indicate:
- employer's name;
- form of ownership and type of economic activity according to OKVED;
- name of the medical organization, actual address of its location and OGRN code;
- type of medical examination - periodic;
- last name, first name, patronymic, date of the employee;
- name of the structural unit;
- name of position, profession or type of work;
- VOPF.
The referral is signed by an authorized representative of the employer, indicating his position, surname and initials. All directions are issued against signature, and records are kept.
5. On the day of the medical examination, the employee submits to the medical organization:
- direction;
- passport or other standard identification document;
- health passport (if available);
- decision of the medical commission that conducted a mandatory psychiatric examination (in cases provided for by Russian legislation).
Periodic medical examination is considered completed if all medical specialists have examined you and all laboratory and functional tests have been completed.
Who pays for periodic medical examinations?
The employer is obliged to conduct periodic medical examinations at his own expense and enter into an agreement with a medical organization licensed to conduct preliminary medical examinations. A permanent medical commission is formed in the medical organization. It is headed by an occupational pathologist. The medical organization is responsible for the quality of medical examinations.
Example of a contract for a medical examination
How are the results of periodic medical examinations of the organization’s employees recorded?
After passing the medical examination, the medical organization issues a conclusion. It states:
- date of issue;
- last name, first name, patronymic, date of birth, gender of the employee;
- employer's name;
- name of the structural unit, position, profession or type of work;
- name of the VOPF;
- MO result (medical contraindications identified, not identified).
The conclusion is signed by the chairman of the medical commission. The document is certified by the seal of a medical organization, which prepares a conclusion in two copies. The first is attached to the outpatient card, the second is given to a person who has undergone a medical examination. Data on the passage of the MO is entered into.
The medical organization, within 30 days after the completion of periodic medical examinations, summarizes their results. Then, together with the territorial bodies of Rospotrebnadzor and representatives of the employer, it compiles in four copies, which are sent within five working days from the date of approval:
- employer;
- to the center of occupational pathology of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
- to the territorial body of Rospotrebnadzor.
One copy of the final act is kept in the medical organization for 50 years.
Extraordinary medical examination
Extraordinary medical examinations are carried out on the basis of medical recommendations specified in the final report of the medical examination.
- at work with harmful or dangerous working conditions, including underground;
- at work related to traffic;
- athletes ();
- working in food industry organizations, public catering and trade, water supply facilities, medical organizations and child care institutions, etc.
The employer has the right to send an employee to an extraordinary medical examination in the following cases:
- at the request of the workers themselves (Article 219 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- in accordance with the recommendations of specialists who participated in preliminary or periodic examinations, as well as for epidemiological indications;
- in accordance with ;
- according to the conclusion of the territorial bodies of Rospotrebnadzor with mandatory justification in the direction of the reasons;
- when a case of nosocomial infection is detected, by decision of specialists from Rospotrebnadzor authorities and institutions.
In the absence of the grounds listed above, the employer does not have the right to send the employee for an extraordinary medical examination without his consent.
Attention
An employee is obliged to immediately notify his immediate or superior manager about a deterioration in his health, including the manifestation of signs of an acute occupational disease (Article 214 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employer, if there are clear signs indicating a decrease in the employee’s ability to work, can send him for an extraordinary medical examination.
Responsibility for failure to undergo a medical examination in the organization
The employer is responsible not only for the timely organization of medical education for employees at its own expense, but also for the admission to work of persons who have not undergone a preliminary or periodic examination, or who are not allowed to work for medical reasons. If inspectors of regulatory authorities establish such a fact, the employer may incur administrative liability.
According to Part 3 of Art. 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, the fine will be as follows:
- for officials - from 15,000 to 25,000 rubles;
- for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from 15,000 to 25,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 110,000 to 130,000 rubles.
The amount of the fine is calculated based on the number of employees who have not completed the mandatory training. If due to lack of medical examination the employee's health will be seriously harmed or his death will occur, the officials will bear the consequences (Article 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
TYPES OF MEDICAL EXAMINATIONS AND PURPOSE OF THEIR CONDUCT
Preliminary medical examinations are carried out upon entry to work in order to determine the compliance of the health status of employees with the assigned work;
Periodic medical examinations are carried out for the purpose of dynamic monitoring of the health status of workers under conditions of exposure to occupational hazards, for the prevention and timely identification of initial signs of occupational diseases, identification of common diseases that prevent the continuation of work with harmful, dangerous substances and production factors, as well as the prevention of accidents.
Guided by the list of general and additional contraindications, the doctor makes a conclusion about the advisability of allowing the person being examined to work.
For example, people suffering from chronic bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, bronchial asthma, severe chronic gastritis, severe vegetative-vascular dystonia should not be hired for work that involves exposure of workers to nitric acid, ammonia and nitrogen oxides.
Another direction of the medical examination is to identify persons who, for health reasons, cannot be entrusted with performing dangerous work (work at height, as well as servicing lifting structures, pressure vessels, work on servicing electrical installations, work directly related to the movement of vehicles, use of explosives, etc.).
In cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, laws and other regulatory legal acts, the EMPLOYER IS OBLIGATED in cases provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, to organize, at its own expense, mandatory preliminary (upon employment) and periodic ( during work) medical examinations (examinations), mandatory psychiatric examinations of workers, extraordinary medical examinations (examinations), mandatory psychiatric examinations of workers at their requests in accordance with medical recommendations with retention of their place of work (position) and average earnings for the duration of the examination specified medical examinations (examinations), mandatory psychiatric examinations (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Workers employed:
Workers engaged in heavy work and work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions (including underground work), as well as in work related to traffic, undergo mandatory preliminary (upon entry to work) and periodic (for persons under the age of 21 - annual) medical examinations (examinations) to determine the suitability of these workers to perform the assigned work and prevent occupational diseases. In accordance with medical recommendations, these employees undergo extraordinary medical examinations (examinations).
Employees of food industry organizations, public catering and trade, water supply facilities, medical and preventive and child care institutions, as well as some other employers undergo the specified medical examinations (examinations) in order to protect public health, prevent the occurrence and spread of diseases.
Harmful and (or) dangerous production factors and work, during the performance of which mandatory preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) are carried out, and the procedure for their conduct are determined by regulatory legal acts approved in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
If necessary, by decision of local authorities, individual employers may introduce additional conditions and indications for mandatory medical examinations (examinations).
Employees engaged in certain types of activities, including those associated with sources of increased danger (with the influence of harmful substances and adverse production factors), as well as those working in conditions of increased danger, undergo a mandatory psychiatric examination at least once every five years in the manner established by the Government Russian Federation. The medical examinations (examinations) and psychiatric examinations provided for in this article are carried out at the expense of the employer (part additionally included from January 1
Persons under the age of eighteen are hired only after a preliminary compulsory medical examination (examination) and subsequently, until they reach the age of eighteen, are annually subject to a compulsory medical examination (examination) (Article 266 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The employer is obliged to suspend from work an employee who has not undergone a mandatory medical examination (examination) in accordance with the established procedure, as well as a mandatory psychiatric examination in cases provided for by federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation (Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
ORGANIZATION OF MEDICAL EXAMINATIONS
Harmful and dangerous production factors and work, during which preliminary and periodic medical examinations are carried out, and the procedure for their implementation are determined by regulatory legal acts approved in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
If necessary, by decision of local authorities, individual organizations may introduce additional conditions for indications for medical examinations.
Temporary List of harmful, dangerous substances and production factors, when working with which preliminary and periodic medical examinations of workers are required.
Temporary list of works, the performance of which requires preliminary and periodic medical examinations of workers.
Preliminary and periodic medical examinations of workers are carried out in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated August 16, 2004 No. 83 “On approval of lists of harmful and (or) dangerous production factors and work, during the performance of which preliminary and periodic medical examinations (examinations) are carried out, and the procedure for conducting these examinations (examinations).
Preliminary and periodic medical examinations of workers are carried out by medical institutions with any form of ownership that have the appropriate license and certificate (type of activity - examination of work ability, type of medical examination - preventive, periodic).
Examinations by a psychiatrist are carried out at a psychoneurological dispensary at the place of permanent residence of the person being examined.
Territorial center Rospotrebnadzor together with the administration (employer) and trade union organization:
annually determines the contingents of persons subject to periodic and preliminary medical examinations by workshop, profession, hazardous, harmful substances and production factors;
exercises control over the completeness of coverage, timeliness and frequency of medical examinations.
The administration of the organization, based on the Lists of contingents received from Rospotrebnadzor authorities, compiles a named list of persons subject to periodic medical examinations, indicating:
FULL NAME. workers,
productions (processes);
harmful production factors to which workers are exposed,
work experience in this profession.
This list is agreed upon with the territorial center of Rospotrebnadzor and certified by its seal and the seal of the organization.
The lists are compiled no later than December 1 of the previous year in at least 3 copies.
The medical and preventive institution, based on the list of employees who are subject to periodic medical examinations received from the administration of the organization, draws up a calendar plan for conducting examinations.
Depending on the degree of harmfulness and level of danger of the work performed, the frequency of inspections is set once every 3, 6, 12, 24 months.
The territorial center, together with the employer, based on the specific sanitary, hygienic and epidemiological situation, has the right to decide to increase the frequency or conduct additional medical examinations.
The employer provides the employee with a referral for a medical examination to provide to the attending physician conducting the examination, a list of harmful, dangerous substances and production factors that affect the employee.
The medical examination data is entered into the outpatient medical record.
Each doctor taking part in the examination gives his opinion on professional suitability and, if indicated, outlines the necessary treatment and preventive measures. Data on the employee’s professional route (organization, workshop, site, profession), length of service, harmful, hazardous substances and production factors and the final conclusion on the suitability of the state of health for the work assigned or another conclusion are placed on a separate sheet. When work activity changes, clarifications and additions are made to the sheet.
The employee has the right to receive a report on his state of health and the absence of contraindications to performing work.
In the case of individual admission, the specified conclusion includes data on the mandatory use of a prosthesis, hearing aid, glasses, etc.
Employees who are contraindicated from working with harmful, hazardous substances and production factors are given a conclusion from the clinical expert commission (CEC) and a copy is sent within three days to the employer who issued the referral.
As prescribed by specialists from the territorial center of Rospotrebnadzor, based on the results of the medical examination, a commission consisting of representatives:
medical institution,
employer,
trade union organization,
State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision-
draws up the Final Commission Report.
THE EMPLOYER (head of the organization) IS RESPONSIBLE:
draw up, within a month after receiving from the Rospotrebnadzor center Lists of contingents of persons subject to preliminary and periodic medical examinations, a name list of such persons indicating the names of production, workshops, professions, harmful, hazardous substances and production factors to which the employee is exposed, length of service in these conditions;
promptly send workers for periodic medical examinations, as well as for extraordinary medical examinations if indicated, indicating in the direction a list of harmful, dangerous substances and production factors that affect workers;
on the basis of an order (instruction), do not allow persons to work who have not passed a preliminary or periodic examination, or who are not allowed to work for medical reasons.